A brand of commercially available canine sustenance, it is formulated to meet the nutritional requirements of dogs at various life stages. The food is typically sold in dry kibble form and may include wet food varieties. It aims to provide a balanced diet through a blend of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. As an example, a specific product may be targeted toward senior dogs, with ingredients chosen to support joint health and cognitive function.
The importance of selecting appropriate nourishment for a dog is paramount to its overall health and well-being. A properly formulated diet can contribute to a healthy coat, optimal weight management, and sustained energy levels. Historically, the availability of specialized dog foods has evolved significantly, moving from simple table scraps to scientifically formulated blends that address specific dietary needs and breed predispositions. The benefits of using such a product include convenience, guaranteed nutrient content, and the potential for addressing specific health concerns.
The following sections will delve into the specific ingredients, nutritional profiles, and potential benefits associated with high-quality canine diets, providing a detailed analysis relevant to discerning pet owners.
Guidance on Canine Nutrition
The following outlines crucial considerations for ensuring a dog receives optimal nutrition, reflecting the principles embodied by quality canine food brands.
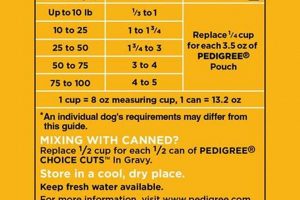
Tip 1: Adhere to Feeding Guidelines: Precise measurements are essential. Overfeeding or underfeeding can lead to health complications. Consult the product’s guidelines and adjust portions based on the dog’s activity level and body condition.
Tip 2: Prioritize Ingredient Quality: Examine the ingredient list carefully. Opt for products where identifiable protein sources (e.g., chicken, beef, fish) are listed first, indicating a higher protein content. Avoid products with excessive fillers or artificial additives.
Tip 3: Consider Life Stage and Activity Level: A puppy requires a different nutritional profile than a senior dog. Select a product formulated specifically for the dog’s life stage and adjust caloric intake based on activity level. Active dogs require more calories and protein than sedentary dogs.
Tip 4: Monitor Body Condition: Regularly assess the dog’s body condition score. Ribs should be easily palpable but not visible. A distinct waistline should be apparent when viewed from above. Adjust feeding amounts to maintain an ideal body condition.
Tip 5: Introduce Dietary Changes Gradually: Abrupt changes in diet can lead to gastrointestinal upset. Transition to a new food slowly by mixing it with the old food over a period of 7-10 days, gradually increasing the proportion of the new food.
Tip 6: Ensure Fresh Water Availability: Adequate hydration is crucial for overall health. Provide access to fresh, clean water at all times.
Tip 7: Consult with a Veterinarian: Seek professional advice from a veterinarian or a board-certified veterinary nutritionist. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the dog’s individual needs and health status.
Implementing these recommendations ensures that the canine companion receives optimal nutrition, contributing to its overall health and well-being.
The subsequent sections will provide more in-depth analysis on the selection and management of canine diets for optimal canine health.
1. Ingredient Composition
Ingredient composition is a fundamental determinant of its overall nutritional value and suitability for a canine. The specific ingredients and their proportions directly impact the dog’s ability to obtain essential nutrients, support bodily functions, and maintain optimal health. For instance, a product listing a named meat source (e.g., chicken, beef, salmon) as the primary ingredient indicates a higher proportion of animal protein, which is crucial for muscle development and maintenance. Conversely, a product relying heavily on grain fillers or by-products may offer limited nutritional benefit and could potentially contribute to digestive issues or allergies in sensitive dogs. The inclusion of specific vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants further enhances the nutritional profile, addressing specific health needs and promoting overall well-being.
The quality and source of ingredients also play a critical role. Ingredients sourced from reputable suppliers with stringent quality control measures minimize the risk of contamination or the presence of harmful substances. Furthermore, the processing methods employed in manufacturing can affect the bioavailability of nutrients. For example, over-processing can denature proteins and reduce their digestibility. The presence or absence of artificial preservatives, colors, and flavors is another important consideration, as these additives may trigger adverse reactions in some dogs. Analyzing the ingredient list and understanding the role of each component is essential for making informed decisions about a canine’s diet.
In summary, ingredient composition is the cornerstone of any canine diet, dictating its nutritional value and potential impact on a dog’s health. A careful evaluation of the ingredients, their sources, and their proportions is essential for selecting a product that meets the dog’s specific needs and supports its overall well-being. Understanding this connection allows owners to provide informed care, promoting optimal health and vitality for their canine companions.
2. Nutritional Adequacy
Nutritional adequacy, in the context of canine diets, refers to the extent to which a product meets the established nutrient requirements for a dog’s specific life stage and activity level. This aspect is paramount because a diet lacking in essential nutrients can lead to various health problems, ranging from stunted growth and weakened immune systems to organ dysfunction and skeletal abnormalities. For example, a growing puppy requires a higher concentration of calcium and phosphorus than an adult dog to support proper bone development. Failure to meet these requirements can result in skeletal deformities. Brands offering a wide product range often formulate diets tailored to these distinct life stages.
Ensuring nutritional adequacy typically involves adherence to guidelines established by organizations such as the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). AAFCO establishes nutrient profiles for different life stages, including growth, maintenance, and reproduction. Products that meet or exceed these profiles are considered nutritionally complete and balanced. However, simply meeting AAFCO standards does not guarantee optimal nutrition. The bioavailability of nutrients and the quality of ingredients also play a significant role. For instance, protein derived from highly digestible sources, such as meat, is generally considered superior to protein derived from plant-based sources, even if both meet the minimum AAFCO requirements. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of nutritional adequacy involves evaluating both compliance with established standards and the quality of ingredients.
In conclusion, nutritional adequacy is a critical component of canine nutrition, directly impacting a dog’s health and well-being. Meeting or exceeding AAFCO standards is a necessary but not sufficient condition for ensuring optimal nutrition. Careful consideration of ingredient quality and bioavailability is also essential. By understanding the principles of nutritional adequacy, owners can make informed decisions about their dogs’ diets and promote optimal health throughout their lives. The selection of diets that align with AAFCO standards ensures the core values of health and well being of the canine companion.
3. Life Stage Formulation
Life stage formulation, a critical aspect of canine nutrition, directly correlates with the health and well-being of dogs at different periods in their lives. Nutritional needs fluctuate significantly from puppyhood to adulthood and into the senior years. Consequently, commercial canine diets, including product offerings, are often formulated to cater to these specific requirements. Failure to account for these variations can lead to nutritional deficiencies or excesses, resulting in adverse health outcomes. For example, a puppy diet necessitates a higher protein and calcium content to support rapid growth and bone development, whereas a senior dog requires a diet lower in calories and supplemented with joint-supporting ingredients. The formulation is intentionally varied to address these diverse needs.
The importance of life stage formulation lies in its ability to provide the precise nutrients required for optimal health and function at each stage of a dog’s life. An adult maintenance formula, for instance, focuses on maintaining lean muscle mass and supporting overall health, while a senior formula prioritizes joint health, cognitive function, and weight management. Ingredient adjustments, such as the inclusion of glucosamine and chondroitin for joint support in senior diets or the increased protein content in puppy diets, exemplify this targeted approach. These adjustments directly impact the dog’s health by addressing the specific physiological challenges associated with each life stage. Moreover, these diets help manage weight and minimize digestive issues.
In summary, life stage formulation is a fundamental principle in canine nutrition, with commercial diets being specifically tailored to meet the changing needs of dogs throughout their lives. Ignoring these considerations can lead to nutritional imbalances and adverse health outcomes. By selecting a diet formulated for the appropriate life stage, owners can ensure that their dogs receive the nutrients required for optimal health and well-being at every phase of their lives, impacting their overall quality of life significantly.
4. Palatability Factors
Palatability factors play a crucial role in determining the success and effectiveness of canine diets, influencing acceptance and consumption. The inherent nutritional value is rendered irrelevant if a dog refuses to consume the food. Therefore, an understanding of these factors is essential when evaluating brands and their suitability for individual animals.
- Aroma Profile
The initial olfactory experience significantly impacts a dog’s willingness to approach and consume the food. Meat-derived aromas and specific volatile compounds enhance palatability. Absence of appealing scents or the presence of off-putting odors (rancidity, spoilage) can deter consumption. Brands often employ techniques to preserve or enhance aroma.
- Texture and Kibble Size
Texture influences mouthfeel and chewing ease. Crunchy kibble can promote dental health and be more appealing to some dogs, while softer textures may be preferred by seniors or dogs with dental issues. Kibble size must be appropriate for the dog’s breed and jaw structure to facilitate proper chewing and prevent choking. Brands offer a variety of textures and sizes to cater to different needs.
- Taste Components
While dogs have fewer taste receptors than humans, they are sensitive to certain flavors. Umami, derived from meat proteins, is generally highly palatable. Sweetness, though less preferred than in humans, can enhance acceptance. Bitterness often deters consumption. Brands utilize flavor enhancers (hydrolyzed proteins, digests) to improve taste profiles.
- Fat Content and Fatty Acid Profile
Fat contributes significantly to palatability, providing flavor and aroma. Certain fatty acids, particularly those found in animal fats, enhance acceptance. However, excessive fat can lead to digestive upset. Brands carefully balance fat content to optimize palatability without compromising digestive health.
The aforementioned factors collectively determine a product’s palatability, impacting the dog’s willingness to consume it consistently. Brands that prioritize research and development to optimize these characteristics are more likely to achieve higher acceptance rates and contribute to improved nutritional outcomes for canine consumers. A multi-faceted approach to palatability ensures that a diet is not only nutritionally sound but also appealing to the intended recipient.
5. Digestibility Metrics
Digestibility metrics provide a quantifiable assessment of how effectively a canine can break down and absorb nutrients from its food. These metrics are particularly relevant when evaluating product quality, as they directly impact the availability of essential nutrients for the animal’s physiological processes. A diet with high digestibility promotes optimal nutrient absorption, minimizing waste and supporting overall health. Consequently, an understanding of digestibility metrics is crucial for informed decision-making regarding canine nutrition.
- Fecal Output and Consistency
Fecal output serves as a direct indicator of digestibility. A diet with high digestibility results in smaller, firmer stools, indicating efficient nutrient absorption and minimal undigested material. Conversely, large, loose stools suggest poor digestibility, with a significant portion of the food passing through the digestive tract without being absorbed. Monitoring fecal output and consistency provides valuable insights into the overall digestibility of a specific diet, informing adjustments to feeding practices or product selection.
- Coefficient of Apparent Digestibility (CAD)
The CAD is a calculated measure of the percentage of nutrients absorbed from the diet. This metric is determined by analyzing the nutrient content of both the food consumed and the feces excreted. A higher CAD indicates a greater proportion of nutrients being absorbed, signifying better digestibility. CAD values are often provided by manufacturers or can be obtained through independent laboratory analysis. Comparative CAD values for different products provide a quantitative basis for assessing their relative digestibility.
- Digestive Enzyme Activity
Assessment of digestive enzyme activity, though less commonly available to the average consumer, provides insights into the breakdown of specific macronutrients. Analysis of amylase (carbohydrate digestion), protease (protein digestion), and lipase (fat digestion) activity in fecal samples can indicate the efficiency of digestive processes. Reduced enzyme activity may suggest impaired digestion, potentially linked to ingredient quality or underlying health conditions.
- Gastrointestinal Transit Time
Gastrointestinal transit time, the duration it takes for food to pass through the digestive tract, can also influence digestibility. Excessively rapid transit may limit nutrient absorption, while excessively slow transit may promote bacterial overgrowth. Factors such as fiber content and ingredient composition can impact transit time. Optimal transit time contributes to efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
These digestibility metrics, while varying in accessibility and complexity, collectively contribute to a comprehensive understanding of how effectively a canine processes and utilizes its diet. Consideration of these metrics, in conjunction with other factors such as ingredient quality and nutritional composition, enables informed selection of products that support optimal digestive health and overall well-being. The principles of optimal digestibility are reflected in the formulation and assessment of canine diets.
6. Health Benefit Claims
Health benefit claims associated with canine diets represent assertions regarding the positive impact of specific products on a dog’s well-being. These claims are intrinsically linked to product formulations, ingredient selection, and purported physiological effects, and necessitate careful scrutiny when evaluating their validity.
- Joint Health Support
Claims regarding joint health support often involve the inclusion of ingredients like glucosamine and chondroitin, purported to aid in cartilage maintenance and reduce inflammation. Real-world examples include formulations targeting senior dogs or breeds predisposed to hip dysplasia. The implication is a potential reduction in pain and improved mobility, though efficacy varies and substantiation through clinical trials is crucial.
- Digestive Health Enhancement
Claims related to digestive health enhancement typically highlight the presence of prebiotics and probiotics, intended to promote a balanced gut microbiome and improve nutrient absorption. Examples include products marketed for dogs with sensitive stomachs or those prone to gastrointestinal upset. The claimed benefit is improved digestive function and reduced incidence of diarrhea or vomiting, though individual responses can vary and the specific strains of probiotics used are significant.
- Coat and Skin Improvement
Claims concerning coat and skin improvement frequently emphasize the inclusion of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, believed to contribute to a healthy skin barrier and a glossy coat. Real-world instances involve formulations marketed for dogs with dry skin, allergies, or dull coats. The claimed benefit is reduced itching, flaking, and improved coat luster, though environmental factors and underlying health conditions also play a role.
- Weight Management Support
Weight management support claims often focus on controlled calorie content, increased fiber levels, and specific protein-to-fat ratios, designed to promote satiety and maintain lean muscle mass. Formulations targeting overweight or obese dogs exemplify this claim. The intended benefit is gradual weight loss and improved body composition, though consistent adherence to feeding guidelines and exercise regimens are essential for success.
The validity of health benefit claims relies on scientific substantiation, ingredient quality, and individual canine responses. While such claims may influence consumer perception and product selection, a comprehensive assessment should involve veterinary consultation and critical evaluation of available evidence to ensure optimal dietary choices are made.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Canine Nutrition
The following section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding canine nutrition, aiming to provide clarity and informed guidance.
Question 1: Is it necessary to purchase life-stage-specific food?
Life-stage-specific formulas address the changing nutritional needs of dogs as they age. Puppies require higher protein and calcium levels for growth, while senior dogs benefit from reduced calorie content and joint support. While not strictly mandatory, such formulas optimize health outcomes.
Question 2: What constitutes a “high-quality” ingredient in canine food?
A high-quality ingredient is typically a named meat source (e.g., chicken, beef, lamb) listed as the primary ingredient, indicating a significant proportion of animal protein. Avoidance of excessive fillers, artificial additives, and vague descriptions (“meat by-products”) is also crucial.
Question 3: How does one assess the nutritional adequacy of a canine diet?
Nutritional adequacy is primarily assessed by verifying compliance with AAFCO (Association of American Feed Control Officials) nutrient profiles for the appropriate life stage. Ingredient quality and digestibility also contribute to overall nutritional value.
Question 4: Are grain-free diets inherently superior to grain-inclusive diets?
Grain-free diets are not inherently superior. While beneficial for dogs with grain sensitivities, they are not necessary for all canines. The overall nutrient profile and ingredient quality are more critical than the presence or absence of grains.
Question 5: What role do supplements play in canine nutrition?
Supplements may be beneficial in specific cases, such as joint support for senior dogs or omega-3 fatty acids for skin health. However, a balanced diet should provide most essential nutrients. Veterinary consultation is recommended before introducing supplements.
Question 6: How frequently should a dog’s diet be changed?
Frequent dietary changes are generally discouraged due to the potential for digestive upset. Changes should be gradual, occurring over 7-10 days, and only when necessary due to medical conditions, life stage transitions, or product availability issues.
The information provided above clarifies central themes in canine nourishment, empowering owners to deliver superior care.
The subsequent section will provide the conclusion.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored various facets of canine nutrition, providing a framework for evaluating the suitability of commercial diets. Key considerations include ingredient composition, nutritional adequacy, life stage formulation, palatability, digestibility, and the validity of health benefit claims. These factors collectively determine a product’s impact on a dog’s overall health and well-being. The information presented equips owners with the knowledge to make informed decisions, weighing the relative merits of different products and aligning dietary choices with the specific needs of their canine companions.
Selecting an appropriate canine diet is a critical responsibility, impacting long-term health outcomes. Continued vigilance in assessing product information, monitoring canine health indicators, and seeking veterinary guidance remains essential. Prioritizing scientific evidence and discerning claims from substantiated facts ensures that dietary choices contribute to the improved health and well-being of canine companions.