This canine nutritional product represents a category of commercially available food designed to meet the dietary needs of domestic dogs, promoting optimal health and well-being through a balanced formulation of essential nutrients. As an example, such a product might contain a precise ratio of protein, carbohydrates, and fats sourced from ingredients like meat, grains, and vegetables.
The significance of such formulations lies in their capacity to support a dog’s physiological functions, including growth, energy production, and immune system maintenance. Historically, advancements in veterinary science and animal nutrition have led to the development of these specialized diets, moving beyond simple scraps to scientifically formulated options.
The remainder of this discussion will elaborate on the specific ingredient profiles, manufacturing processes, and potential health implications associated with this type of pet food. Further analysis will also cover consumer considerations and the regulatory framework governing its production and distribution.
Guidance for Selecting a Canine Diet
The following recommendations aim to provide clarity and actionable insights for responsible canine owners in choosing a nutritionally appropriate diet.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ingredient Quality: Scrutinize the ingredient list, emphasizing whole food sources like named meats (e.g., chicken, beef), whole grains (e.g., brown rice, oats), and recognizable vegetables. Avoid products with excessive fillers (e.g., corn, soy) or ambiguous meat by-products.
Tip 2: Assess Protein Content: Ensure an adequate protein level, particularly for active dogs or puppies. Protein should constitute a significant portion of the diet, supporting muscle development and overall health. Consult with a veterinarian to determine the optimal protein percentage for a specific dog’s life stage and activity level.
Tip 3: Evaluate Fat Composition: Healthy fats are essential for energy and coat health. Look for sources like fish oil, flaxseed, or sunflower oil. Be mindful of excessive fat content, which can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
Tip 4: Check for Essential Nutrients: Verify that the diet includes essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, B vitamins, and minerals like calcium and phosphorus, crucial for bone health and overall well-being.
Tip 5: Consider Life Stage and Activity Level: Select a formulation specifically tailored to the dog’s life stage (puppy, adult, senior) and activity level (sedentary, active, working). These factors influence the nutrient requirements and caloric needs.
Tip 6: Monitor Dog’s Response: Closely observe the dog’s overall health, coat condition, energy levels, and stool quality after introducing a new diet. Any adverse reactions, such as digestive upset or skin irritation, warrant a reevaluation of the selected food.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes informed decision-making, contributing to the dog’s long-term health and vitality. A conscientious approach to canine nutrition enhances quality of life and potentially mitigates future health concerns.
The subsequent section will explore specific brands and formulations within the canine food market, providing a comparative analysis of their nutritional profiles.
1. Nutritional Adequacy
Nutritional adequacy, in the context of canine diets, refers to the extent to which a food product meets the established nutritional requirements for dogs, as defined by recognized authorities such as the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). This is a critical consideration when evaluating the suitability of any canine food.
- Macronutrient Balance
Macronutrient balance pertains to the correct proportion of protein, fat, and carbohydrates. A diet lacking sufficient protein may lead to muscle loss and impaired immune function, while excessive fat can contribute to obesity. An optimally formulated canine diet contains these macronutrients in ratios that support the dog’s metabolic needs, age, and activity level. For example, a working dog may require a higher fat content for sustained energy.
- Micronutrient Sufficiency
Micronutrient sufficiency involves the presence of essential vitamins and minerals in adequate quantities. Deficiencies in vitamins like Vitamin D or minerals like calcium can result in skeletal abnormalities and other health problems. An AAFCO-approved canine food will contain a vitamin and mineral premix designed to meet these minimum requirements. The specific needs vary depending on the dog’s life stage.
- Amino Acid Profile Completeness
Amino acid profile completeness focuses on the presence of all essential amino acids, which dogs cannot synthesize themselves and must obtain from their diet. A protein source lacking in one or more essential amino acids is considered incomplete and may lead to health issues over time. Meat-based protein sources are generally considered complete, whereas plant-based sources may require careful combination to ensure a full amino acid profile.
- Digestibility and Bioavailability
Digestibility and bioavailability assess the extent to which the nutrients in the food can be digested and absorbed by the dog’s body. A food may contain adequate levels of nutrients, but if these nutrients are not readily absorbed, the dog will not benefit fully. Factors like ingredient processing methods and the presence of anti-nutritional factors can impact digestibility. Highly digestible ingredients lead to better nutrient utilization and reduced waste.
The concept of nutritional adequacy is central to evaluating any canine food. Choosing a product that demonstrably meets established nutritional standards, possesses a balanced macronutrient profile, provides sufficient micronutrients, contains complete protein sources, and is easily digestible is paramount to ensuring canine health and well-being. The next phase involves comparing specific products against these criteria.
2. Ingredient Sourcing
Ingredient sourcing, with respect to canine nutrition, directly impacts the overall quality, safety, and nutritional value of the final product. Transparency and accountability in sourcing practices are therefore essential for producing a high-quality canine diet.
- Geographic Origin and Traceability
The geographic origin of ingredients determines potential exposure to environmental contaminants and variations in nutrient profiles. For example, fish sourced from polluted waters may contain higher levels of heavy metals. Traceability systems allow manufacturers to track ingredients back to their source, ensuring accountability and enabling rapid response in case of contamination events. The ability to verify the origin of protein sources, grains, and other components is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
- Supplier Certifications and Audits
Supplier certifications, such as those from organizations focused on food safety and quality management, indicate adherence to established standards in agricultural practices, processing, and handling. Regular audits of suppliers by manufacturers or independent third parties verify compliance with these standards and identify potential risks. These audits may cover aspects such as pesticide use, storage conditions, and sanitation practices, minimizing the risk of contamination and ensuring consistent quality.
- Ingredient Processing Methods
The processing methods used to prepare ingredients can significantly affect their nutritional value and digestibility. For instance, excessive heat treatment may denature proteins and reduce the bioavailability of certain vitamins. Minimally processed ingredients, such as whole grains and gently cooked meats, retain more of their natural nutrients and are often more digestible. Transparency regarding processing techniques allows consumers to make informed choices based on their preferences and the specific needs of their dogs.
- Ethical and Sustainable Practices
Ethical sourcing considers the welfare of animals used in the production of meat and poultry, as well as the environmental impact of agricultural practices. Sustainable sourcing aims to minimize resource depletion, reduce pollution, and support biodiversity. For example, using sustainably harvested fish or pasture-raised livestock reflects a commitment to responsible resource management and can appeal to ethically conscious consumers.
These facets of ingredient sourcing underscore its pivotal role in defining the characteristics and perceived value of “optim dog food”. A rigorous approach to sourcing ensures the delivery of a safe, nutritious, and ethically produced canine diet. Subsequent discussions will address the impact of manufacturing processes on these raw ingredients.
3. Life Stage Formulation
The concept of life stage formulation is fundamentally linked to the nutritional optimization of canine diets. Commercial dog foods designed for specific life stages aim to address the varying physiological needs of dogs throughout their lives, from puppyhood through adulthood and into their senior years. The rationale centers on the premise that a puppy requires more calories and certain nutrients to support growth, while a senior dog needs fewer calories and ingredients tailored to aging organs.
- Puppy-Specific Formulations
Puppy-specific diets prioritize ingredients supporting rapid growth and development. These formulations typically contain higher levels of protein and fat to fuel energy demands and muscle development. Additionally, they emphasize calcium and phosphorus in appropriate ratios to promote bone growth and density. An example would be a formulation with increased DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid, which is believed to support brain and vision development during this critical phase. Improper nutrition during puppyhood can lead to skeletal abnormalities and stunted growth, demonstrating the importance of tailored formulas.
- Adult Maintenance Formulations
Adult maintenance diets are designed to sustain optimal health and weight in mature dogs. These formulations generally contain balanced levels of protein, fat, and carbohydrates to meet the dog’s daily energy requirements without promoting excessive weight gain. Fiber content is often adjusted to support digestive health and maintain regular bowel movements. A typical ingredient profile might include named meat sources, whole grains, and added vitamins and minerals, reflecting a focus on sustained health and vitality in adulthood. These diets aim to mitigate risks such as obesity and related metabolic disorders.
- Senior-Specific Formulations
Senior-specific diets address the unique needs of aging dogs, focusing on maintaining muscle mass, supporting joint health, and promoting cognitive function. These formulations typically contain lower calorie levels to combat decreased activity levels and potential weight gain. Added glucosamine and chondroitin may support joint health, while antioxidants like vitamin E and vitamin C can help protect against cellular damage associated with aging. A modified protein level helps preserve lean muscle mass, which naturally declines with age. These considerations reflect the emphasis on longevity and quality of life during the senior years.
- Breed-Specific Considerations
While not strictly life stage formulation, breed-specific diets represent a nuanced approach to canine nutrition. Certain breeds exhibit predispositions to specific health conditions or have unique metabolic requirements. For instance, large breed puppies benefit from controlled levels of calcium and phosphorus to prevent rapid growth that can contribute to skeletal problems. Similarly, breeds prone to certain digestive issues may benefit from easily digestible ingredients and added prebiotics and probiotics. These specialized formulations highlight the recognition that genetics and breed characteristics can significantly influence nutritional needs.
The adaptation of canine diets to match the specific life stage and, in some cases, the breed of the animal underscores the importance of a tailored approach to nutrition. This level of specificity in “optim dog food” aims to optimize health outcomes and potentially extend the animal’s lifespan. The selection process should involve consulting with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate formulation for the individual dog, considering its age, breed, activity level, and any underlying health conditions.
4. Digestibility Factors
Digestibility factors represent a crucial determinant of the nutritional value derived from canine diets. The efficiency with which a dog can break down and absorb nutrients directly impacts its overall health and well-being. Consequently, the digestibility of “optim dog food” directly influences its ability to provide the necessary building blocks for cellular function, energy production, and immune system maintenance. Poor digestibility can lead to nutrient deficiencies, even if the food’s nutritional profile appears adequate on paper. For example, a diet high in indigestible plant fibers may hinder the absorption of essential minerals, resulting in health complications despite seemingly sufficient mineral content.
The composition of canine food significantly affects its digestibility. Higher quality protein sources, such as named meat meals, are generally more digestible than plant-based proteins. Similarly, the inclusion of easily digestible carbohydrates, like rice or oats, facilitates efficient energy absorption. The use of advanced processing techniques, such as extrusion, can improve the digestibility of starches by breaking down complex carbohydrate structures. Furthermore, the presence of prebiotics and probiotics can promote a healthy gut microbiome, which aids in digestion and nutrient absorption. An imbalance in the gut microbiome, caused by indigestible ingredients or poor quality food, can lead to digestive upset, malabsorption, and a compromised immune system. As a practical application, owners should observe their dog’s stool quality as an indicator of digestibility; consistent, well-formed stools typically indicate good digestive efficiency.
In summary, digestibility factors are integral to realizing the potential benefits of “optim dog food”. Optimizing digestibility through careful ingredient selection, appropriate processing methods, and the inclusion of beneficial gut flora support ultimately enhances nutrient absorption and contributes to improved canine health. The challenge lies in accurately assessing and ensuring digestibility, which requires careful consideration of ingredient quality, processing techniques, and the individual dog’s digestive capabilities. Further research into ingredient-specific digestibility and the role of the gut microbiome will continue to refine our understanding and improve the formulation of canine diets.
5. Veterinary Approval
The endorsement of a canine diet by veterinary professionals carries significant weight, reflecting a level of scrutiny and validation regarding the food’s nutritional adequacy and overall suitability for canine consumption. Veterinary approval is not a universally standardized certification but rather represents a complex interplay of factors, including ingredient evaluation, formulation analysis, and clinical observations.
- Ingredient Assessment and Safety Validation
Veterinarians possess the expertise to evaluate ingredient lists, identifying potential allergens, toxins, or components of questionable nutritional value. Approval often hinges on the exclusion of harmful additives and the inclusion of ingredients known to support canine health. For instance, a veterinarian might scrutinize the source of protein, evaluating whether it is a named meat source or an ambiguous “animal by-product.” The presence of artificial colors or preservatives would also be subject to critical assessment. The implications of this assessment include minimizing the risk of adverse reactions and ensuring the food provides a safe and beneficial dietary option.
- Nutritional Profile Evaluation Against Established Standards
Veterinarians assess whether a particular canine diet meets or exceeds the nutritional guidelines established by recognized organizations such as the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). This evaluation considers the balance of macronutrients (protein, fat, carbohydrates) and the presence of essential micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). A veterinarian will determine if the food provides adequate levels of these nutrients to support various life stages, activity levels, and specific health conditions. The importance of this evaluation lies in preventing nutritional deficiencies or excesses that could lead to health problems.
- Clinical Observation and Empirical Evidence
While laboratory analysis provides valuable data, veterinary approval is often informed by real-world clinical observations. Veterinarians may monitor the health and well-being of dogs consuming a particular diet, assessing factors such as coat condition, energy levels, digestive health, and body weight. Positive clinical outcomes contribute to a favorable assessment of the food’s efficacy. Empirical evidence, gathered through case studies and anecdotal observations, adds further support to the claims made by the manufacturer.
- Reputation and Transparency of the Manufacturer
Veterinarians often consider the reputation and transparency of the company producing the canine diet. Factors such as the company’s history, commitment to quality control, and willingness to disclose ingredient sources and manufacturing processes can influence a veterinarian’s assessment. A company with a strong track record of producing safe and nutritious pet food is more likely to receive veterinary approval. Transparency in labeling and communication fosters trust and allows veterinarians to make informed recommendations.
The multifaceted nature of veterinary approval underscores the importance of seeking professional guidance when selecting “optim dog food”. While a veterinarian’s endorsement does not guarantee optimal health for every dog, it represents a valuable indication of nutritional quality and safety, bolstering confidence in the product’s suitability for canine consumption. Reliance on veterinary expertise contributes to informed decision-making and promotes responsible pet ownership.
6. Allergen Control
Allergen control, a critical aspect of “optim dog food” formulation, directly addresses the potential for adverse immune responses in canines triggered by specific food ingredients. The presence of allergens can precipitate a range of symptoms, from mild skin irritation to severe gastrointestinal distress. Therefore, a proactive approach to allergen control is paramount in ensuring the safety and tolerability of a commercial canine diet. For instance, if “optim dog food” contains beef and a dog is allergic to beef, it’s important to prevent any harm to dogs allergic to it. By avoiding common allergenic ingredients, such as beef, dairy, wheat, soy, and chicken, manufacturers can reduce the likelihood of triggering allergic reactions in sensitive dogs. The exclusion of potential allergens is a crucial measure in promoting canine well-being.
Practical applications of allergen control strategies include the development of limited-ingredient diets, which minimize the number of potential allergens present in the formulation. These diets often feature novel protein sources, such as duck, venison, or rabbit, which are less likely to elicit an immune response in dogs with sensitivities to more common proteins. Additionally, hydrolyzing proteins, a process that breaks down protein molecules into smaller, less allergenic fragments, can be implemented. Careful ingredient sourcing and rigorous testing protocols are also essential components of allergen control. Manufacturers must ensure that ingredients are free from cross-contamination with potential allergens during processing and handling.
In summary, allergen control is a fundamental consideration in the design and production of “optim dog food.” By understanding the potential for allergic reactions and implementing proactive strategies to minimize allergen exposure, manufacturers can create safer and more tolerable diets for canines. The challenges lie in identifying all potential allergens and implementing effective measures to prevent contamination. A thorough understanding of allergen control principles is essential for responsible pet food formulation and contributes significantly to the overall health and well-being of the canine population.
Frequently Asked Questions about Canine Nutrition
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding optimal dietary choices for dogs, providing evidence-based information to assist owners in making informed decisions.
Question 1: What are the most critical nutrients for a healthy canine diet?
The cornerstone of a healthy canine diet rests on the adequate provision of protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Protein supports muscle development and repair; fat provides energy and aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins; carbohydrates supply readily available energy; and vitamins and minerals facilitate various physiological processes.
Question 2: How does “optim dog food” differ for puppies versus adult dogs?
Formulations designed for puppies typically contain higher levels of protein and fat to fuel rapid growth and development. They also include appropriate ratios of calcium and phosphorus to support bone mineralization. Adult formulations generally contain a balanced nutrient profile to maintain optimal health and weight.
Question 3: What ingredients should be avoided in canine diets?
Canine diets should ideally exclude artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives, as these additives offer no nutritional value and may trigger adverse reactions in some dogs. Excessive amounts of fillers, such as corn and soy, should also be avoided as they can dilute the nutritional density of the food.
Question 4: How can a dog owner assess the quality of “optim dog food?”
A dog owner can assess the quality by examining the ingredient list, prioritizing whole food sources like named meats and whole grains. Certification from organizations such as AAFCO further validates the nutritional adequacy of the food. Observing the dog’s overall health, coat condition, and stool quality can also provide valuable insights.
Question 5: What is the role of fiber in “optim dog food?”
Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health by adding bulk to the stool and facilitating regular bowel movements. Certain types of fiber can also act as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial bacteria in the gut and supporting a healthy microbiome.
Question 6: Should “optim dog food” be supplemented with additional vitamins or minerals?
In most cases, a commercially formulated canine diet that meets AAFCO standards provides all the necessary vitamins and minerals. However, in certain circumstances, such as during pregnancy or illness, a veterinarian may recommend supplementation. Routine supplementation without veterinary guidance is generally not advisable.
In conclusion, informed canine dietary choices are essential for promoting health and longevity. Careful attention to ingredient quality, nutritional balance, and individual canine needs contributes to optimal well-being.
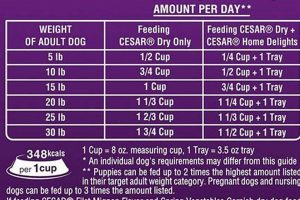
The subsequent section will delve into practical feeding guidelines and portion control strategies for canines.
Conclusion
This examination of “optim dog food” has elucidated the multifaceted factors that contribute to its formulation, nutritional value, and overall suitability for canine consumption. Key considerations encompass ingredient sourcing, life stage formulation, digestibility factors, veterinary approval, and allergen control. Each of these elements plays a critical role in ensuring that the dietary needs of dogs are met in a safe and effective manner.
The long-term health and well-being of canines depend significantly on informed dietary choices. Continued vigilance regarding product quality, coupled with ongoing research into canine nutritional requirements, remains paramount. Further advancements in understanding the canine microbiome and the impact of specific nutrients will undoubtedly refine dietary recommendations in the future, contributing to improved canine health outcomes.