Cesar dog food is a commercially available brand of wet pet food marketed toward small breed dogs. Formulated with a blend of meat, vegetables, and grains in gravy or sauce, it presents a convenient, pre-portioned feeding option. The nutritional adequacy of this food hinges on its ability to meet the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) guidelines for canine nutrition, specifically regarding protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
The appeal of prepared dog food lies in its convenience and readily available nature, freeing owners from the time and effort required for homemade diets. It is vital for pet owners to understand the ingredients and nutritional profile to ensure that the selected food supports the dog’s overall health and well-being. Historical trends show increasing reliance on commercial diets, necessitating a critical examination of product formulations.
The ensuing discussion will examine the ingredients commonly found in Cesar dog food, analyze its nutritional content relative to canine dietary needs, consider potential benefits and drawbacks, and explore alternative feeding options.
Guidance on Evaluating Cesar Dog Food
The following suggestions are designed to assist in the assessment of Cesar dog food as a dietary option for canines.
Tip 1: Evaluate Ingredient Quality: Prioritize identification of named meat sources (e.g., chicken, beef) as primary ingredients. Generic terms like “meat by-products” offer less clarity regarding origin and nutritional value.
Tip 2: Assess Nutritional Adequacy: Confirm that the product meets AAFCO nutrient profiles for the dog’s life stage (growth, adult maintenance, or all life stages). This indicates that the food provides a complete and balanced diet.
Tip 3: Consider Caloric Content: Small breeds have unique caloric needs. Adhere to feeding guidelines on the packaging, adjusting as needed based on the dog’s activity level and body condition.
Tip 4: Scrutinize Added Ingredients: Be mindful of artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. While present in some formulations, they offer limited nutritional benefit and may be undesirable for some owners.
Tip 5: Monitor Digestive Response: Observe the dog’s stool quality and consistency after introducing the food. Changes in bowel movements may indicate intolerance or difficulty digesting specific ingredients.
Tip 6: Consult with a Veterinarian: Obtain professional guidance from a veterinarian, particularly for dogs with existing health conditions or dietary sensitivities. They can offer tailored recommendations.
Tip 7: Rotate Food Choices: Introduce variety with other high-quality dog food brands to ensure a well-rounded nutritional intake and prevent potential sensitivities from developing.
Careful examination of ingredient lists, nutritional information, and veterinary consultation is imperative for making informed decisions regarding canine nutrition.
The subsequent section will consolidate the findings and present a conclusive overview of the topic.
1. Ingredient Quality
Ingredient quality is a primary determinant in assessing the overall value of any dog food. Regarding Cesar dog food, a detailed analysis of constituent ingredients is essential to ascertain its suitability for canine consumption. The presence of high-quality components significantly contributes to the nutritional value and potential health benefits, while lower-quality ingredients may raise concerns about digestibility and long-term well-being.
- Named Meat Sources
The presence of clearly identified meat sources (e.g., chicken, beef, lamb) as primary ingredients is indicative of higher quality. These provide essential amino acids necessary for muscle development and overall bodily function. Absence of such named sources, replaced by generic terms like “meat by-products,” raises concerns about the origin and quality of the protein source. Cesar formulations should be examined to verify the prominence and specificity of meat ingredients.
- Grain Content and Quality
Grain inclusion in dog food serves as a carbohydrate source, providing energy. However, the type and quality of grains are crucial. Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, oatmeal) offer greater nutritional value compared to refined grains (e.g., white rice, corn). Furthermore, some dogs may exhibit sensitivities or allergies to certain grains. The grain composition within Cesar recipes should be evaluated in light of potential allergenic properties and overall nutritional contribution.
- Presence of Artificial Additives
Artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives are often incorporated into processed dog foods to enhance palatability and extend shelf life. While these additives may improve a product’s appeal to consumers, they offer no nutritional benefit and may be detrimental to canine health. Some artificial additives have been linked to allergic reactions and other adverse effects. A thorough ingredient list review is necessary to identify and assess the impact of these additives in Cesar dog food.
- Fat Sources and Quality
Fats are vital for energy, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. High-quality fat sources, such as fish oil or poultry fat, provide essential fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6, which contribute to skin and coat health. The inclusion of unspecified “animal fat” or other less desirable fat sources may compromise the overall quality of the product. Examining the fat composition of Cesar dog food reveals the quality and potential benefits of its lipid content.
In conclusion, the evaluation of ingredient quality within Cesar dog food formulations is paramount. The presence of named meat sources, the type and quality of grains, the inclusion of artificial additives, and the sources of fats all contribute to the overall assessment. A discerning approach to ingredient analysis is critical in determining whether Cesar dog food aligns with the dietary needs and health considerations of individual dogs.
2. Nutritional Completeness
Nutritional completeness is a crucial determinant when evaluating if a commercially available pet food, such as Cesar, is suitable for canine consumption. This term indicates that the food provides all essential nutrientsproteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and mineralsin the correct proportions to meet a dog’s life stage requirements, as defined by organizations like AAFCO. A deficiency in any of these areas can lead to various health problems, ranging from stunted growth and weakened immunity to organ dysfunction. For example, insufficient protein intake can result in muscle loss, while a lack of calcium can cause skeletal abnormalities, particularly in growing puppies. Therefore, a food that fails to meet established nutritional standards cannot be considered a sound dietary option.
Cesar dog food, like other commercial diets, should declare compliance with AAFCO nutrient profiles on its packaging. This declaration implies that the formulation has undergone testing or has been formulated to meet established nutritional benchmarks. However, it is imperative to scrutinize the ingredient list and guaranteed analysis to confirm the presence and amounts of essential nutrients. An example would be evaluating if the food provides adequate levels of taurine, an amino acid vital for heart health, especially in certain breeds prone to dilated cardiomyopathy. Furthermore, even if a food meets the minimum requirements, some veterinarians advocate for higher levels of certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, to promote optimal health. Therefore, going beyond mere compliance with AAFCO guidelines is often advisable.
In summary, nutritional completeness is a fundamental criterion for assessing if Cesar dog food is a satisfactory choice for dogs. While AAFCO compliance serves as a basic indicator, a thorough evaluation of the ingredient list and guaranteed analysis, coupled with veterinary consultation, is necessary to ensure that the food truly supports a dog’s specific dietary needs and promotes long-term health. The practical significance of this understanding is underscored by the direct link between dietary inadequacies and potential health complications, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making in pet nutrition.
3. Caloric Density
Caloric density, referring to the number of calories per unit weight or volume of food, plays a critical role in determining the appropriateness of Cesar dog food for individual canines. This characteristic dictates the amount of food required to meet a dog’s daily energy needs and directly influences weight management.
- Portion Control and Weight Management
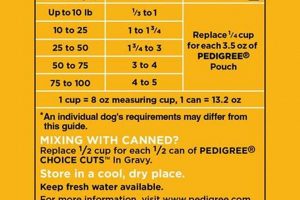
High caloric density necessitates smaller portions to avoid overfeeding, a factor particularly relevant for small breeds, the target demographic for Cesar. Failure to accurately measure portions can lead to weight gain and associated health risks such as diabetes, arthritis, and cardiovascular disease. Conversely, low caloric density may require larger portions, which may be impractical for dogs with limited appetites or digestive sensitivities. The caloric density of Cesar formulations must be considered alongside feeding guidelines and individual metabolic rates.
- Metabolic Rate and Activity Level
A dog’s metabolic rate and activity level are primary determinants of daily caloric requirements. Active dogs require more calories per day than sedentary dogs. Cesar dog food, regardless of its ingredient composition, must provide sufficient calories to fuel activity without promoting weight gain in less active animals. Therefore, the caloric density should align with the intended use case, adjusting portions based on the dog’s lifestyle.
- Ingredient Composition and Energy Content
The macronutrient composition of Cesar recipes, particularly the proportion of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins, significantly impacts caloric density. Fats contribute more than twice the calories per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. Formulations high in fat will inherently possess a higher caloric density. The ingredient list should be scrutinized to understand the relative contribution of each macronutrient to the overall energy content.
- Life Stage Considerations
Puppies, adult dogs, and senior dogs have varying caloric needs. Growing puppies require higher caloric density to support rapid growth and development, while senior dogs may benefit from lower caloric density to prevent weight gain associated with reduced activity levels. Cesar dog food’s suitability hinges on matching the caloric density to the life stage of the dog, necessitating different formulations or adjustments to portion sizes.
In conclusion, caloric density is a fundamental factor to consider when evaluating if Cesar dog food is a suitable dietary choice. Accurate assessment of caloric density, coupled with careful monitoring of portion sizes and adjustments based on activity level and life stage, is essential for maintaining optimal weight and preventing associated health problems in canines.
4. Added Ingredients
The presence and nature of added ingredients are critical factors in evaluating the suitability of Cesar dog food. While essential nutrients are vital, understanding non-essential additives is equally important in determining overall product quality and potential impact on canine health.
- Artificial Colors
Artificial colors, such as Red 40, Yellow 5, and Blue 2, are incorporated to enhance the visual appeal of the food to pet owners. These additives provide no nutritional value and have been linked to hyperactivity and allergic reactions in some dogs. The presence of artificial colors in Cesar recipes raises concerns about prioritizing aesthetics over canine well-being.
- Artificial Flavors
Artificial flavors are used to improve palatability, encouraging consumption, particularly among picky eaters. However, these flavors often mask lower-quality ingredients and may not accurately represent the true nutritional content of the food. The reliance on artificial flavors can lead to the acceptance of otherwise unpalatable food, potentially undermining healthy dietary choices.
- Artificial Preservatives
Artificial preservatives, including BHA, BHT, and ethoxyquin, extend shelf life by preventing oxidation and spoilage. While effective in preserving food, these preservatives have been associated with potential health risks, including cancer and organ damage, in some studies. Safer, natural alternatives like Vitamin E (tocopherols) and Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) are available, making the use of artificial preservatives a point of concern.
- Fillers
Fillers, such as corn gluten meal and cellulose, add bulk to the food without contributing significant nutritional value. These ingredients can displace more nutritious components and may be difficult for some dogs to digest. High levels of fillers suggest a lower overall quality and potentially reduced bioavailability of essential nutrients.
The evaluation of added ingredients in Cesar dog food necessitates careful consideration of their purpose, potential risks, and available alternatives. While some additives may serve a functional role in palatability or preservation, the presence of artificial colors, flavors, preservatives, and excessive fillers detracts from the product’s overall quality and raises concerns about its suitability for promoting long-term canine health.
5. Digestive Health
Digestive health directly influences nutrient absorption and overall well-being in canines. The composition of Cesar dog food, including ingredient digestibility and the presence of potential irritants, significantly affects a dog’s gastrointestinal function. If the food contains ingredients poorly digested by a particular dog, it may result in diarrhea, vomiting, or flatulence. For example, some dogs exhibit sensitivities to specific grains or artificial additives often found in commercially prepared dog foods. Poor digestive health, therefore, can impede the nutritional benefits ostensibly offered by the food.
A dog’s breed, age, and individual sensitivities play vital roles in determining digestive response. Cesar dog food, formulated primarily for small breeds, may not be appropriate for larger dogs with differing dietary requirements. Senior dogs with compromised digestive systems may struggle to process certain ingredients. Observing stool quality, consistency, and frequency after introducing a new food, such as Cesar, offers valuable insights into its digestibility. A smooth transition and a consistent, healthy stool indicate good tolerance, whereas changes suggest potential incompatibility. Probiotics are increasingly included to enhance gut health.
Ultimately, assessing whether Cesar dog food promotes or hinders digestive health requires careful observation, consideration of individual canine characteristics, and, if necessary, consultation with a veterinarian. Failure to address digestive issues resulting from dietary choices can lead to chronic health problems and diminished quality of life. Thus, digestive health emerges as a pivotal consideration in the overall evaluation of a specific dog food’s suitability.
6. Veterinarian Approval
Veterinarian approval serves as a critical validation point when assessing the suitability of any commercial dog food, including Cesar. This endorsement signifies that a qualified animal health professional has reviewed the food’s formulation, considered its potential benefits and risks, and deemed it appropriate, or at least not detrimental, for canine consumption. It is a point to be noted with “is cesar food good for dogs”.
- Individualized Health Assessment
Veterinarians possess the expertise to evaluate a dog’s specific health status, considering factors such as breed predispositions, existing medical conditions, and age-related changes. This individualized assessment informs dietary recommendations, ensuring that the selected food aligns with the dog’s unique needs. A dog with kidney disease, for example, requires a diet with restricted phosphorus levels, a consideration a veterinarian would address during their evaluation of Cesar dog food.
- Nutritional Adequacy Verification
While AAFCO guidelines provide minimum nutrient requirements, veterinarians can assess whether a food exceeds or falls short of optimal levels for a particular dog. They scrutinize ingredient lists and guaranteed analyses to ensure the presence and appropriate quantities of essential nutrients. This extends beyond basic compliance, focusing on promoting optimal health through targeted nutrition. If a dog has a skin condition, a veterinarian might recommend a Cesar formula supplemented with omega fatty acids.
- Addressing Owner Concerns and Misconceptions
Veterinarians serve as a reliable source of information, dispelling myths and addressing owner concerns surrounding canine nutrition. They can objectively evaluate marketing claims and provide evidence-based guidance. An owner might express concerns about artificial additives in Cesar; a veterinarian can provide context on the potential risks and benefits, and offer alternative options if necessary.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment
Veterinarian approval is not a one-time event. Regular checkups allow for ongoing monitoring of a dog’s health and dietary response. If a dog exhibits adverse reactions to Cesar dog food, such as digestive upset or weight changes, the veterinarian can adjust the diet accordingly. This iterative process ensures that the food remains appropriate as the dog’s needs evolve.
In conclusion, veterinarian approval provides a crucial layer of assurance when evaluating the suitability of Cesar dog food. Their expertise in assessing individual health needs, verifying nutritional adequacy, addressing owner concerns, and monitoring dietary response ensures that the food aligns with the dog’s well-being. While not a guarantee of universal suitability, it provides a valuable safeguard against potential dietary deficiencies or adverse reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Cesar Dog Food
The following questions and answers address common inquiries and concerns regarding the suitability of Cesar dog food for canine consumption. Information is presented in a factual and objective manner.
Question 1: Is Cesar dog food nutritionally complete for all life stages?
Cesar dog food formulations may or may not be nutritionally complete for all life stages. Pet owners should carefully examine the product packaging to verify compliance with AAFCO nutrient profiles for the dog’s specific life stage (growth, adult maintenance, or all life stages).
Question 2: Does Cesar dog food contain artificial additives?
Some Cesar dog food recipes contain artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. The presence of these additives should be carefully considered, as they offer no nutritional benefit and may cause adverse reactions in sensitive dogs. Ingredient lists should be thoroughly reviewed.
Question 3: Is Cesar dog food suitable for large breed dogs?
Cesar dog food is primarily marketed towards small breed dogs. Large breed dogs have different nutritional requirements, particularly during puppyhood, and may not receive adequate nutrition from Cesar formulations. Consultation with a veterinarian is recommended.
Question 4: Can Cesar dog food contribute to weight gain?
Due to its caloric density, particularly in certain recipes, Cesar dog food can contribute to weight gain if portion sizes are not carefully controlled. Pet owners should adhere to feeding guidelines and adjust portions based on the dog’s activity level and body condition.
Question 5: Does Cesar dog food address specific dietary sensitivities?
While some Cesar dog food recipes may be formulated without common allergens, the brand does not explicitly cater to specialized dietary needs. Dogs with known sensitivities or allergies may require alternative diets formulated with limited ingredients or hydrolyzed proteins.
Question 6: Should Cesar dog food be the sole source of nutrition for a dog?
Whether Cesar dog food can serve as a sole source of nutrition depends on the specific formulation and the dog’s individual needs. If the food meets AAFCO nutrient profiles for the dog’s life stage and the dog exhibits no adverse reactions, it may be suitable as a primary diet. However, variety and supplementation may be beneficial in certain cases.
This FAQ section provides essential information for assessing the suitability of Cesar dog food. It is advisable to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate dietary choices for individual canine companions.
The following section will present a summary of the article, emphasizing the key points in determining if “is cesar food good for dogs”.
Concluding Remarks on Cesar Dog Food Evaluation
The preceding analysis has explored multifaceted considerations pertinent to the central question: is Cesar food good for dogs? The assessment encompasses ingredient quality, nutritional completeness, caloric density, added ingredients, digestive health implications, and the critical role of veterinary consultation. Formulations vary, and while some recipes may meet basic nutritional requirements, the presence of artificial additives and reliance on potentially less digestible ingredients warrant careful scrutiny. Suitability hinges on individual canine needs, life stage, and potential sensitivities. Not all dog foods work the same for all dogs.
Ultimately, determining the appropriateness of Cesar dog food necessitates a discerning approach. Comprehensive evaluation, combined with professional veterinary guidance, ensures informed dietary decisions that prioritize canine health and well-being. Responsible pet ownership demands diligent assessment of dietary choices, recognizing that optimal nutrition contributes significantly to overall quality of life.