This dietary option for canines is characterized by small, bite-sized pieces formulated to mirror the ancestral diet of dogs, emphasizing raw, whole-food ingredients. Its composition typically includes meat, bones, and organs, alongside fruits and vegetables, presented in a convenient, pre-portioned format.
Such a diet aims to provide canines with optimal nutrition, mirroring the nutritional profile they would encounter in a natural setting. Proponents suggest benefits such as improved digestion, enhanced coat quality, increased energy levels, and strengthened immune systems. The concept of providing raw, minimally processed food to dogs has gained traction in recent years, driven by a growing awareness of canine nutritional needs and a desire to move away from traditional processed kibble.
The following sections will delve into the specific ingredients, manufacturing processes, nutritional advantages, and potential drawbacks associated with this particular type of canine nourishment, as well as considerations for its safe and effective implementation in a dog’s feeding regimen.
Tips for Utilizing This Canine Dietary Option
The following guidelines provide information on integrating this specific type of canine nutrition into a dog’s diet safely and effectively.
Tip 1: Gradual Transition: Introduce the new food gradually over a period of 7-10 days. Begin by mixing a small amount with the existing diet, slowly increasing the proportion of the new food while decreasing the old.
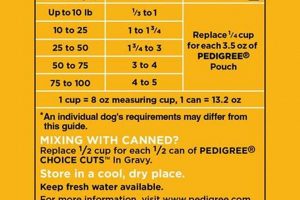
Tip 2: Portion Control: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended feeding guidelines based on the dog’s weight, age, and activity level. Monitor body condition and adjust portions accordingly to maintain a healthy weight.
Tip 3: Food Safety: Practice proper food handling techniques. Thaw frozen portions in the refrigerator, not at room temperature. Wash hands, bowls, and surfaces thoroughly after handling raw food to prevent bacterial contamination.
Tip 4: Storage: Store this type of dog food in the freezer until ready to use. Once thawed, it should be refrigerated and consumed within 2-3 days to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage.
Tip 5: Variety and Rotation: Consider incorporating a variety of protein sources and formulations to ensure a balanced nutrient intake. Rotating between different recipes can help prevent the development of sensitivities or allergies.
Tip 6: Monitor Stool Quality: Observe stool consistency and frequency. Changes in stool can indicate an adjustment period or potential dietary sensitivities. Consult with a veterinarian if issues persist.
Tip 7: Consult with a Veterinarian: Before making significant dietary changes, consult with a veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist. This is especially important for puppies, pregnant or lactating dogs, and dogs with pre-existing health conditions.
Implementing these guidelines can contribute to a successful and beneficial transition to this particular canine dietary approach, ensuring the dog receives optimal nutrition and maintains overall health.
The concluding section will summarize the critical considerations discussed and offer concluding remarks regarding the utilization of this feeding method.
1. Ingredient Composition
Ingredient composition forms the foundational element of this specific canine food product. The types and proportions of ingredients directly influence its nutritional value, digestibility, and potential health effects. For example, a product emphasizing muscle meat without sufficient organ meat or bone may lack essential vitamins and minerals like calcium or certain B vitamins. Conversely, an overabundance of organ meat could lead to excessive levels of fat-soluble vitamins. The selection of protein sources beef, chicken, lamb, etc. can affect palatability and the likelihood of triggering allergies or sensitivities in individual dogs.
A significant aspect of the ingredient list is the inclusion of fruits and vegetables. These components supply fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients. However, the specific types and quantities are critical. For instance, a high proportion of starchy vegetables may contribute to excessive carbohydrate intake, while inadequate fiber could compromise digestive health. Furthermore, the source and processing of ingredients matter. Products using grass-fed, pasture-raised meats and organic produce typically command a higher price point, reflecting perceived benefits related to animal welfare and reduced exposure to pesticides or antibiotics.
In summary, a thorough evaluation of the ingredient composition is essential when considering this feeding option. Understanding the specific ingredients, their proportions, and their sources enables informed decisions regarding the suitability and potential benefits for individual dogs. Failure to adequately assess this aspect can result in nutritional imbalances or adverse health outcomes. Therefore, consumers should meticulously examine the ingredient list and nutritional analysis provided by the manufacturer, and ideally consult with a veterinary nutritionist to determine the optimal formulation for their dog’s specific needs.
2. Nutritional Adequacy
Nutritional adequacy represents a critical consideration when evaluating any canine diet, and this holds particularly true for raw, nugget-style formulations. Ensuring a diet meets the established nutritional requirements for dogs is paramount for maintaining their health and well-being. This is achieved through careful formulation and adherence to established guidelines.
- AAFCO Guidelines
The Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) sets standards for pet food nutrient profiles. Compliance with AAFCO guidelines indicates that a food provides complete and balanced nutrition for a specific life stage, such as growth, maintenance, or all life stages. This compliance is often indicated on the product label. For example, a statement might read, “This product is formulated to meet the nutritional levels established by the AAFCO Dog Food Nutrient Profiles for all life stages.” Without such a statement, the nutritional adequacy of the product is questionable.
- Macronutrient Ratios
Appropriate ratios of protein, fat, and carbohydrates are essential. A diet too high in fat could lead to weight gain and pancreatitis, while insufficient protein might result in muscle loss. The ideal ratios vary depending on the dog’s age, breed, activity level, and health status. For instance, a highly active working dog requires a different macronutrient profile than a sedentary senior dog. These specific needs drive the proper composition of the diet.
- Micronutrient Balance
Vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in various physiological processes. Deficiencies or excesses of certain micronutrients can lead to health problems. For example, inadequate calcium and phosphorus can impair bone development in puppies, while excessive vitamin A can cause skeletal abnormalities. Ensuring a balanced blend of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, vitamin E, B vitamins, zinc, and iron, is therefore key to canine health.
- Bioavailability of Nutrients
The form in which nutrients are presented impacts their absorption and utilization by the body. Raw diets may offer certain nutrients in a more bioavailable form compared to highly processed kibble. However, it’s essential to ensure that these nutrients are present in sufficient quantities and are readily absorbed by the dog’s digestive system. The sourcing and processing of ingredients can affect bioavailability, and some nutrients may require supplementation to meet the dog’s needs effectively.
Addressing these facets is essential for confirming the nutritional soundness of this feeding method. By verifying AAFCO compliance, assessing macronutrient ratios, ensuring micronutrient balance, and considering bioavailability, one can ascertain whether this form of canine nourishment provides complete and balanced nutrition. Consultation with a veterinary nutritionist is recommended to tailor dietary choices to individual dog’s needs.
3. Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes employed in the production of this dog food directly affect product safety, nutrient retention, and overall quality. Raw diets, by their nature, present specific challenges compared to traditional kibble production. Stringent controls are required to mitigate the risk of bacterial contamination, such as Salmonella or E. coli. These controls typically involve sourcing ingredients from reputable suppliers with rigorous testing protocols, maintaining clean production environments, and implementing validated pathogen reduction strategies. For instance, high-pressure processing (HPP) is often used to eliminate harmful bacteria without significantly affecting nutrient content or palatability. Improper handling or inadequate sanitation during manufacturing can introduce pathogens, posing a health risk to pets and their owners.
Beyond safety, manufacturing techniques also influence nutrient bioavailability and preservation. Harsh processing methods, such as high-heat extrusion used in kibble production, can degrade heat-sensitive vitamins and alter protein structures, potentially reducing their digestibility. Conversely, gentle methods like freeze-drying or minimal heating aim to preserve the natural nutrients present in raw ingredients. The grinding and mixing processes also play a crucial role. Over-processing can damage cell structures, leading to nutrient loss and increased susceptibility to oxidation. Therefore, manufacturers often employ specialized equipment and techniques to minimize nutrient degradation and maintain the integrity of raw ingredients.
Ultimately, the choice of manufacturing processes determines the safety, nutritional value, and shelf-life of this food. Consumers should seek out products from manufacturers that prioritize food safety and employ methods that preserve nutrient integrity. Transparency regarding manufacturing processes is also a key indicator of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. Understanding the potential impact of different manufacturing techniques empowers consumers to make informed decisions about the food they feed their pets, promoting their health and well-being.
4. Storage Requirements
Proper storage is paramount for maintaining the safety and nutritional integrity of this canine food. Due to its composition of raw ingredients, including meat, organs, and potentially raw bones, this dietary option presents unique storage challenges compared to processed dry kibble.
- Freezing Temperatures
The primary storage method involves maintaining the product in a frozen state until shortly before feeding. This is critical for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can proliferate rapidly at room temperature or even refrigerated temperatures. Frozen storage effectively suspends bacterial activity, preventing spoilage and minimizing the risk of foodborne illness. Improper freezing, such as inadequate temperature control or thawing and refreezing, can compromise the product’s safety and nutritional value.
- Thawing Procedures
Safe thawing practices are essential. The recommended method is to thaw the product in the refrigerator for a period of time sufficient to achieve complete thawing. This slow thawing process minimizes the temperature range conducive to bacterial growth. Thawing at room temperature is strongly discouraged, as it allows bacteria to multiply rapidly. Once thawed, the product should be used within a specific timeframe, typically 24 to 48 hours, to ensure freshness and safety. Unused portions should be discarded after this period.
- Refrigeration Guidelines
While frozen storage is the primary method, refrigeration plays a secondary role after thawing. The thawed product must be stored in the refrigerator at temperatures below 40F (4C) to further inhibit bacterial growth. Proper refrigeration practices include storing the food in airtight containers to prevent cross-contamination and minimize exposure to air, which can accelerate spoilage. The storage time in the refrigerator should be strictly adhered to, and any signs of spoilage, such as unusual odors or discoloration, warrant immediate disposal of the product.
- Preventing Cross-Contamination
Rigorous hygiene practices are essential to prevent cross-contamination between the raw food and other items in the refrigerator or freezer. Dedicated storage containers should be used solely for the product, and these containers should be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized after each use. Contact between the raw food and other foods, particularly those intended for human consumption, should be avoided to minimize the risk of spreading harmful bacteria. Proper handwashing after handling the food is also crucial for preventing the transmission of pathogens.
Adherence to these storage requirements is not merely a suggestion but a necessity for mitigating the inherent risks associated with raw food diets. Failure to follow proper storage and handling procedures can lead to bacterial contamination, foodborne illness in both pets and humans, and a reduction in the nutritional value of the product. Therefore, consumers must be fully aware of and committed to these guidelines when choosing this feeding option for their canines.
5. Potential Risks
The use of raw, nugget-style dog food introduces specific potential risks that necessitate careful consideration and mitigation strategies. These risks primarily stem from the raw nature of the ingredients and the inherent challenges in maintaining consistent safety standards throughout the production and handling process.
- Bacterial Contamination
Raw meat and organs, common components of this diet, can harbor pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter. While dogs’ digestive systems are generally more resilient to these bacteria than those of humans, the presence of these pathogens poses a risk to both the animal and individuals handling the food. Contamination can occur during processing, packaging, or storage, and improper handling at home can further exacerbate the risk. Symptoms of bacterial infection in dogs can include vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and fever.
- Nutritional Imbalance
While proponents of raw diets emphasize their natural and wholesome qualities, formulating a nutritionally complete and balanced raw diet requires specialized knowledge. Homemade raw diets, or commercially prepared diets that deviate from established nutritional guidelines, can lead to deficiencies or excesses of essential nutrients. For example, improper ratios of calcium and phosphorus can impair bone development in growing puppies, while inadequate levels of vitamin D can lead to various health problems. Ensuring adherence to AAFCO guidelines and consulting with a veterinary nutritionist are essential for mitigating this risk.
- Parasitic Infections
Raw meat can also contain parasites, such as tapeworms or roundworms, which can infect dogs upon ingestion. Freezing the meat prior to feeding can help kill some parasites, but not all. Thoroughly cooking the meat eliminates the risk of parasitic infection but negates the intended benefits of a raw diet. Regular deworming medication, prescribed by a veterinarian, is often recommended for dogs consuming raw food to prevent or treat parasitic infections.
- Bone Fragments
The inclusion of raw bones is a common feature, intended to provide calcium and promote dental health. However, bone fragments can pose a choking hazard or cause damage to the digestive tract. Sharp bone shards can lacerate the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, leading to serious complications. The risk of bone-related injuries can be reduced by feeding appropriately sized bones and supervising the dog during consumption. Cooked bones should never be fed, as they are more brittle and prone to splintering.
These potential risks underscore the importance of careful sourcing, manufacturing, and handling practices associated with the use of this diet. While proponents emphasize the purported benefits of raw feeding, a thorough understanding and mitigation of these risks are essential for ensuring the health and safety of canine companions and their human handlers. Informed decision-making, based on sound veterinary advice and a commitment to safe food handling practices, is crucial when considering this alternative feeding strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Primal Nuggets Dog Food
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the utilization of this specific canine dietary approach. These answers aim to provide clarity and informed guidance to assist in decision-making.
Question 1: Are Primal Nuggets Dog Food nutritionally complete for all life stages?
Nutritional completeness varies depending on the specific formulation. It is imperative to verify that the product label includes a statement indicating compliance with AAFCO (Association of American Feed Control Officials) nutrient profiles for the intended life stage of the dog (e.g., growth, maintenance, all life stages). Products lacking this statement may not provide complete and balanced nutrition.
Question 2: What are the primary ingredients in Primal Nuggets Dog Food?
The ingredient composition typically includes a combination of raw meat (muscle meat, organ meat), bones (or bone meal), fruits, and vegetables. Specific ingredients will vary depending on the product formulation. A thorough review of the ingredient list on the product packaging is recommended to ascertain the precise components.
Question 3: How should Primal Nuggets Dog Food be stored to maintain safety and quality?
This product should be stored frozen until shortly before feeding. Thawing should occur in the refrigerator, not at room temperature. Once thawed, it should be refrigerated and used within 24-48 hours to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination. Proper handling and hygiene practices are essential to prevent cross-contamination.
Question 4: What are the potential risks associated with feeding Primal Nuggets Dog Food?
Potential risks include bacterial contamination (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli), nutritional imbalances (if not properly formulated), and the presence of bone fragments that could pose a choking hazard or cause digestive tract injury. Adhering to proper handling and storage guidelines and consulting with a veterinarian can mitigate these risks.
Question 5: How does Primal Nuggets Dog Food differ from traditional dry kibble?
This type of dog food differs from dry kibble primarily in its ingredient composition and processing methods. This diet consists of raw, minimally processed ingredients, while kibble undergoes high-heat extrusion. Proponents suggest this minimizes nutrient degradation and preserves the natural enzymes and nutrients present in the ingredients. However, kibble offers convenience and a longer shelf life.
Question 6: Is it necessary to supplement Primal Nuggets Dog Food with additional vitamins or minerals?
If the specific formulation is AAFCO-approved and complete and balanced for the dog’s life stage, supplementation is generally not necessary. However, individual dogs may have unique nutritional needs based on their health status, breed, or activity level. Consultation with a veterinarian or veterinary nutritionist is recommended to determine whether supplementation is appropriate.
These FAQs address fundamental inquiries related to this canine diet. It is critical to diligently examine product labels, adhere to safety guidelines, and consult with veterinary professionals to make well-informed decisions regarding canine nutrition.
The subsequent section will provide concluding remarks and summarize the key considerations discussed within this document.
Concluding Remarks on Primal Nuggets Dog Food
This exploration has illuminated crucial facets of “primal nuggets dog food,” encompassing ingredient sourcing, manufacturing rigor, storage protocols, and inherent risks. Comprehension of these factors is paramount when considering this dietary approach for canines. AAFCO compliance, nutrient bioavailability, and mitigation of bacterial contamination represent essential considerations that should not be overlooked.
The decision to incorporate “primal nuggets dog food” into a canine’s diet warrants careful deliberation. Responsible pet ownership demands a commitment to informed choices, guided by veterinary expertise and an unwavering focus on animal welfare. Continued research and transparent communication within the pet food industry are vital for ensuring the safety and efficacy of all dietary options available to canine companions. This approach serves as the bedrock for optimal canine health and well-being.