The selection of optimal canine nutrition plays a pivotal role in mitigating excessive hair loss. This specific category of food is formulated with ingredients known to promote coat health and reduce the volume of shed hair. An example would be a diet rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, often derived from fish oil or flaxseed, which contribute to skin hydration and hair follicle strength.
Addressing the issue of excessive shedding offers several advantages. It reduces the amount of time spent cleaning up loose fur, contributing to a cleaner home environment. More importantly, a healthy coat is indicative of overall canine well-being. Historically, anecdotal evidence has supported the link between diet and coat condition, but modern veterinary science has increasingly validated this connection through nutritional research.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific nutrients that contribute to reduced shedding, explore commercially available options and their respective ingredients, and provide guidance on selecting the most appropriate diet based on individual canine needs and breed predispositions.
Selecting Canine Diets to Minimize Shedding
The following recommendations address dietary considerations that can significantly influence the amount of hair a canine sheds. These are presented as actionable guidelines for informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Prioritize Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids: These essential fatty acids are fundamental for maintaining skin health and coat luster. Sources include fish oil, flaxseed oil, and certain vegetable oils. A balanced ratio is crucial; consult product labeling for specific concentrations.
Tip 2: Evaluate Protein Content and Source: An adequate protein intake is necessary for hair growth and repair. High-quality animal-based protein sources, such as chicken, beef, or fish, are generally more digestible and bioavailable for canines compared to plant-based alternatives.
Tip 3: Incorporate Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as Vitamin E and Vitamin C, contribute to overall cellular health, including skin cells. These can be found in various fruits and vegetables that are sometimes included in canine diets.
Tip 4: Minimize Potential Allergens: Certain ingredients, such as wheat, corn, or soy, can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible canines, leading to skin irritation and increased shedding. Consider hypoallergenic or limited-ingredient diets if allergies are suspected.
Tip 5: Ensure Adequate Hydration: Water is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and hydration. Ensure constant access to fresh, clean water. Dry food can contribute to dehydration if not balanced with sufficient water intake.
Tip 6: Consider Breed-Specific Needs: Certain breeds are predisposed to skin and coat issues. Research breed-specific dietary recommendations to address potential nutritional deficiencies or sensitivities.
Tip 7: Monitor for Ingredient Quality: Opt for diets that list specific ingredients rather than vague terms like “meat by-products.” Higher-quality ingredients are typically more digestible and nutrient-dense.
Implementing these recommendations can lead to a noticeable reduction in shedding and an improvement in the overall health and appearance of the canine coat. Consistent dietary management is essential for achieving sustained results.
The subsequent section will offer a comparative analysis of commonly available canine diets, focusing on their suitability for addressing shedding concerns.
1. Omega Fatty Acids
Omega fatty acids play a critical role in canine dermatological health, directly influencing the quality and retention of the coat. Their inclusion in canine diets formulated to minimize shedding is based on demonstrable physiological benefits.
- Reduction of Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), possess anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds can mitigate skin inflammation resulting from allergies, environmental factors, or autoimmune responses. Reduced inflammation minimizes pruritus (itching), which in turn lessens the likelihood of excessive scratching and subsequent hair loss. For example, diets supplemented with fish oil, a rich source of EPA and DHA, have been shown to improve skin conditions associated with allergic dermatitis.
- Enhancement of Skin Barrier Function
Omega-6 fatty acids, such as linoleic acid, are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the epidermal barrier. This barrier protects against moisture loss and the invasion of allergens and pathogens. A compromised skin barrier leads to dryness, irritation, and increased shedding. Dietary supplementation with omega-6 fatty acids strengthens the skin’s protective function, reducing transepidermal water loss and promoting a healthier coat. Vegetable oils, like sunflower oil, provide a source of linoleic acid.
- Improvement of Hair Follicle Health
Adequate omega fatty acid intake contributes to the health of hair follicles, the structures from which hair grows. These nutrients support the production of sebum, a natural oil that lubricates and protects the hair shaft. Healthy hair follicles produce stronger, more resilient hairs that are less prone to breakage and shedding. Diets deficient in omega fatty acids can result in dry, brittle hair that is easily shed.
- Modulation of the Immune Response
Omega fatty acids can modulate the immune system, preventing overreactions that contribute to skin inflammation and hair loss. In canines with autoimmune skin conditions, such as lupus erythematosus, omega-3 fatty acids may help to dampen the inflammatory response, reducing the severity of symptoms and minimizing shedding. This immunomodulatory effect underscores the importance of omega fatty acids in managing dermatological conditions associated with excessive hair loss.
The incorporation of omega fatty acids into canine diets designed to manage shedding represents a targeted nutritional approach. By reducing inflammation, strengthening the skin barrier, promoting follicle health, and modulating the immune response, these nutrients contribute significantly to a healthier coat and reduced hair loss. Consideration of the source and ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is crucial for optimizing their efficacy in mitigating shedding.
2. High-Quality Protein
The inclusion of high-quality protein in canine diets is directly correlated with coat health and the reduction of excessive shedding. Protein serves as the fundamental building block for hair, and its source and digestibility significantly impact its efficacy in maintaining a healthy coat.
- Amino Acid Profile
Hair is composed primarily of keratin, a fibrous structural protein rich in specific amino acids, including cysteine and methionine. High-quality protein sources provide a complete and balanced amino acid profile, ensuring that the canine’s body has all the necessary components to synthesize keratin efficiently. Diets deficient in essential amino acids can lead to brittle, weak hair that is prone to breakage and shedding. Animal-based protein sources, such as chicken, beef, or fish, generally offer a more complete amino acid profile compared to plant-based alternatives. An example is a diet with chicken as the primary protein source, providing adequate levels of cysteine for robust hair growth.
- Digestibility and Bioavailability
The digestibility of the protein source determines the extent to which the canine can absorb and utilize the amino acids. Highly digestible protein sources are more efficiently broken down in the digestive tract, allowing for greater absorption of essential amino acids. Ingredients with low digestibility result in a significant portion of the protein being excreted, reducing its contribution to coat health. Protein meals, if rendered using appropriate methods, can offer concentrated protein sources with good digestibility. Factors such as processing techniques and the presence of antinutritional factors can influence protein digestibility.
- Impact on Skin Health
Protein deficiency can compromise the integrity of the skin, leading to dryness, inflammation, and increased susceptibility to infections. The skin acts as a protective barrier, and its health is directly linked to the condition of the coat. Adequate protein intake supports the production of collagen and other structural proteins essential for maintaining skin elasticity and hydration. A canine with protein deficiency may exhibit a dull, dry coat and increased shedding due to underlying skin issues. High-quality protein contributes to a robust skin barrier, reducing the likelihood of dermatological problems that exacerbate hair loss.
- Muscle Mass and Overall Health
While directly impacting coat health, protein also supports overall muscle mass and immune function. A healthy canine is better equipped to maintain a healthy coat. Protein deficiency can lead to muscle wasting and a weakened immune system, indirectly contributing to poor coat condition and increased shedding. A diet formulated with adequate high-quality protein supports both coat health and overall well-being, creating a synergistic effect that minimizes hair loss.
The selection of canine nutrition that delivers high-quality protein is paramount for minimizing excessive shedding. By ensuring a complete amino acid profile, optimizing digestibility, supporting skin health, and promoting overall well-being, high-quality protein plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy and resilient canine coat.
3. Antioxidant Support
Antioxidant support within canine nutrition plays a significant role in maintaining coat health and minimizing excessive shedding. Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between free radical production and antioxidant defenses, can damage cells, including those within the skin and hair follicles. This damage can lead to inflammation, weakening of the hair shaft, and ultimately, increased hair loss. Canine diets rich in antioxidants mitigate this oxidative stress, promoting healthier skin and a more resilient coat. For example, Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant, protects cell membranes from damage and supports skin hydration, reducing dryness and subsequent shedding. Similarly, Vitamin C contributes to collagen synthesis, essential for the structural integrity of the skin and hair follicles.
The practical application of this understanding is evident in the formulation of premium canine diets. These diets often include a blend of antioxidants derived from natural sources, such as fruits and vegetables. Beta-carotene from carrots, lycopene from tomatoes, and flavonoids from blueberries are examples of phytonutrients that contribute to antioxidant protection. These ingredients help to neutralize free radicals generated by metabolic processes, environmental pollutants, and inflammatory responses. A diet deficient in antioxidants may leave the canine vulnerable to oxidative damage, resulting in a dull, brittle coat and increased shedding.
In summary, antioxidant support is a critical component of canine nutrition designed to minimize shedding. By combating oxidative stress, antioxidants promote healthier skin and hair follicles, leading to a stronger, more resilient coat. The inclusion of antioxidant-rich ingredients in canine diets represents a proactive approach to maintaining dermatological health and reducing excessive hair loss. Challenges exist in determining the optimal antioxidant blend and dosage for individual canines, highlighting the need for personalized dietary recommendations based on age, breed, and health status.
4. Hydration
Adequate hydration is an often-underestimated factor in maintaining canine coat health and minimizing shedding. The relationship between water intake and coat condition is physiological and directly impacts the integrity of the skin and hair follicles.
- Skin Elasticity and Moisture Retention
Water is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and moisture content. Dehydration can lead to dry, brittle skin that is more prone to irritation and damage. Compromised skin integrity directly affects the health of the hair follicles, increasing the likelihood of hair breakage and subsequent shedding. An adequately hydrated canine exhibits supple skin, indicating sufficient moisture levels to support a healthy coat. For instance, canines on dry food diets may require increased water intake to compensate for the lack of moisture in their food.
- Nutrient Transport and Metabolic Processes
Water facilitates the transport of essential nutrients to the skin and hair follicles, supporting metabolic processes necessary for hair growth and repair. Adequate hydration ensures that cells receive the building blocks required for keratin production and follicle maintenance. Dehydration can impede nutrient delivery, leading to deficiencies that compromise coat health. The efficiency of nutrient absorption and utilization is intrinsically linked to hydration levels. Proper water intake ensures that nutrients from the selected canine diet are effectively delivered to the coat.
- Toxin Elimination
Water plays a crucial role in flushing out toxins from the body. These toxins can accumulate and contribute to inflammation and skin irritation, exacerbating shedding. Efficient kidney function, reliant on adequate hydration, removes waste products that can negatively impact skin health. Canines with compromised kidney function or those not consuming sufficient water may experience a buildup of toxins, leading to dermatological issues. Hydration, therefore, supports the body’s natural detoxification processes, indirectly promoting a healthier coat.
- Sebum Production and Coat Lubrication
Sufficient hydration supports the production of sebum, the natural oil that lubricates and protects the hair shaft. Sebum helps to maintain coat moisture, preventing dryness and breakage. Dehydration can reduce sebum production, resulting in a dry, lackluster coat that is more prone to shedding. The balance between water intake and sebum production is critical for maintaining optimal coat condition. Canines that consume adequate water exhibit a glossy, well-lubricated coat, indicative of healthy sebum production.
These facets illustrate the interconnectedness of hydration and coat health, emphasizing the importance of ensuring sufficient water intake in canines. When evaluating the suitability of a canine diet for minimizing shedding, hydration status must be considered alongside nutritional composition. A comprehensive approach addresses both the dietary components and the water intake necessary for optimal coat health, collectively contributing to the reduction of excessive shedding.
5. Allergen Avoidance
The principle of allergen avoidance is integral to the selection of canine nutrition designed to minimize shedding. Allergic reactions, triggered by specific food ingredients, often manifest as dermatological issues, including pruritus (itching), inflammation, and subsequent hair loss. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: exposure to an allergen provokes an immune response that compromises the skin’s integrity, leading to increased shedding. Therefore, identifying and eliminating potential allergens from a canine’s diet is a critical component of managing and mitigating excessive hair loss. For example, a canine sensitive to poultry may experience improved coat condition and reduced shedding upon switching to a fish-based diet. Similarly, eliminating grains like wheat or corn can alleviate allergic symptoms in susceptible individuals, reducing inflammation and promoting a healthier coat.
The importance of allergen avoidance extends beyond simply reducing shedding. Chronic allergic reactions can lead to secondary skin infections and overall discomfort for the animal. Limited-ingredient diets, formulated with a single protein source and a minimal number of additional ingredients, facilitate the identification of potential allergens. Novel protein sources, such as venison or kangaroo, are often utilized to minimize the likelihood of triggering a reaction in canines previously exposed to common allergens. Real-life examples illustrate the practical significance of this approach: a canine diagnosed with atopic dermatitis exhibiting severe pruritus and hair loss demonstrates significant improvement following the implementation of a hypoallergenic diet prescribed by a veterinarian. Ongoing monitoring and, in some instances, allergy testing are essential for maintaining optimal coat health through allergen avoidance.
In conclusion, allergen avoidance is a fundamental consideration in selecting canine nutrition to prevent shedding. By proactively identifying and eliminating potential allergens, it is possible to mitigate allergic reactions, promote healthier skin, and reduce excessive hair loss. Challenges remain in accurately identifying allergens, necessitating careful observation and, in some cases, veterinary intervention. However, the practical benefits of allergen avoidance underscore its importance in the broader context of canine dermatological health and well-being, reinforcing the connection between diet and coat condition.
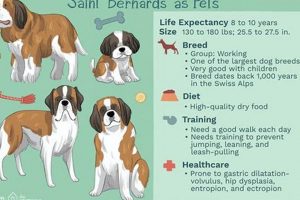
6. Breed Specificity
Canine breeds exhibit significant variations in coat type, skin sensitivity, and metabolic requirements. These breed-specific differences directly influence the selection of appropriate nutrition to minimize shedding and maintain optimal coat health. Therefore, a generalized approach to canine nutrition is often inadequate, and dietary choices should be tailored to the specific needs of each breed.
- Coat Type and Grooming Needs
Different coat types, such as long-haired, short-haired, double-coated, and wire-haired, have distinct shedding patterns and grooming requirements. Breeds with thick undercoats, like Huskies and German Shepherds, are prone to seasonal shedding, necessitating diets that support hair follicle health and reduce excessive hair loss during these periods. Conversely, breeds with minimal shedding, such as Poodles or Bichon Frises, may benefit from diets formulated to enhance coat shine and texture rather than primarily focusing on shedding reduction. Dietary adaptations, such as increased omega fatty acid supplementation during shedding season for double-coated breeds, exemplify the practical application of this facet.
- Prevalence of Skin Conditions
Certain breeds exhibit a higher predisposition to specific skin conditions, such as allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, or sebaceous adenitis. These conditions can exacerbate shedding and necessitate specialized diets. For example, Shar Peis are prone to skin fold dermatitis, requiring diets that support immune function and minimize inflammation. Similarly, breeds with a higher incidence of allergies, such as Labrador Retrievers, may benefit from hypoallergenic diets formulated with limited ingredients and novel protein sources to avoid triggering allergic reactions. Understanding the breed-specific risks for skin conditions is crucial for selecting appropriate nutrition.
- Metabolic and Digestive Efficiency
Variations in metabolic rate and digestive efficiency can influence the canine’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients essential for coat health. Some breeds, such as Great Danes, are prone to digestive sensitivities and may require diets formulated with highly digestible protein sources and prebiotics to support gut health. Efficient nutrient absorption is critical for ensuring that the canine receives the necessary building blocks for keratin synthesis and hair follicle maintenance. Addressing breed-specific digestive challenges can indirectly contribute to improved coat condition and reduced shedding.
- Body Size and Energy Requirements
Canine size and activity level influence energy requirements and nutrient needs. Larger breeds require diets formulated to support bone and joint health, as well as adequate protein for muscle maintenance. Insufficient protein intake can compromise coat health and increase shedding. Similarly, highly active breeds require diets with higher caloric density to meet their energy demands. Adjusting the diet based on breed-specific energy requirements ensures that the canine receives the necessary nutrients for overall health, including coat maintenance. A balanced approach considers both the caloric and nutrient needs specific to each breed.
These considerations underscore the importance of tailoring canine nutrition to the specific needs of each breed. While general principles of coat health, such as omega fatty acid supplementation and high-quality protein sources, remain relevant, the specific implementation and dietary formulation should be adapted to the breed’s unique characteristics. This individualized approach optimizes coat health and minimizes shedding, contributing to the overall well-being of the canine.
7. Ingredient Quality
The relationship between ingredient quality and the effectiveness of canine diets in minimizing shedding is fundamental. Ingredient quality directly influences nutrient bioavailability, digestibility, and the potential for adverse reactions, all of which impact coat health. Lower-quality ingredients often contain fillers, by-products, and artificial additives that offer limited nutritional value and may contribute to inflammation or allergic responses, thereby exacerbating shedding. Conversely, high-quality ingredients provide essential nutrients in a readily digestible form, supporting skin health, hair follicle function, and overall coat integrity. The inclusion of named meat sources, whole grains, and identifiable fruits and vegetables signifies a commitment to ingredient quality. Diets formulated with these components are more likely to deliver the necessary nutrients to promote a healthy coat and minimize hair loss. An example would be a diet listing “chicken” as the primary ingredient versus “poultry by-product meal,” with the former indicating a higher-quality protein source.
The practical significance of ingredient quality extends to the management of canine allergies and sensitivities. Many commercial diets contain common allergens, such as corn, wheat, and soy, which can trigger dermatological reactions in susceptible canines. These reactions often manifest as pruritus, inflammation, and increased shedding. Limited-ingredient diets, formulated with a single protein source and minimal potential allergens, mitigate this risk. The careful selection of high-quality ingredients minimizes the likelihood of adverse reactions, promoting a healthier coat and reducing excessive hair loss. Ongoing monitoring and, if necessary, veterinary consultation can help identify and eliminate specific allergens, further optimizing dietary management. In a practical setting, canines with previously diagnosed food allergies often demonstrate significant improvement in coat condition and reduced shedding following a diet change to a limited-ingredient formula with high-quality, novel protein sources.
In summary, ingredient quality is a critical determinant of a canine diet’s ability to minimize shedding. The selection of high-quality ingredients promotes nutrient bioavailability, reduces the risk of allergic reactions, and supports overall coat health. Challenges remain in navigating the complexities of pet food labeling and discerning true ingredient quality. However, a proactive approach that prioritizes recognizable, nutrient-dense ingredients is essential for achieving optimal coat health and minimizing excessive hair loss in canines, reinforcing the importance of understanding and interpreting pet food labels effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding dietary strategies to minimize canine shedding. These answers aim to provide clarity and guidance based on current veterinary nutritional understanding.
Question 1: Can dietary modification entirely eliminate canine shedding?
Dietary modification can significantly reduce excessive shedding, but it is unlikely to eliminate the natural shedding process entirely. Canines shed as part of a normal hair growth cycle, and this cycle is influenced by genetics, environment, and overall health. Dietary interventions primarily focus on strengthening hair follicles and promoting skin health, thereby minimizing abnormal or excessive hair loss.
Question 2: How long does it take to see results after changing to a new diet intended to reduce shedding?
Visible results typically require several weeks to months. The canine hair growth cycle is relatively slow, and it takes time for new, healthier hair to replace existing hair. Improvement in skin condition may be noticeable sooner, but a full assessment of coat health requires sustained dietary management for at least 8-12 weeks. Consistent adherence to the new dietary plan is essential for achieving optimal results.
Question 3: Are grain-free diets inherently superior for minimizing shedding?
Grain-free diets are not inherently superior for minimizing shedding unless the canine has a specific grain allergy or sensitivity. While some canines benefit from grain-free formulations due to reduced allergen exposure, grains themselves are not inherently detrimental to coat health. The overall nutritional profile, including the quality of protein, fat, and micronutrients, is more critical than the presence or absence of grains.
Question 4: What role do supplements play in reducing canine shedding?
Supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can play a beneficial role in reducing shedding, particularly when added to a balanced diet. Omega-3 fatty acids support skin hydration and reduce inflammation, contributing to improved coat health. However, supplements should not be used as a substitute for a nutritionally complete and balanced diet. Consultation with a veterinarian is recommended before initiating any supplementation regimen.
Question 5: Is it possible to over-supplement a canine’s diet with nutrients intended to reduce shedding?
Yes, over-supplementation is possible and can be detrimental to canine health. Excessive intake of certain nutrients, such as vitamin A or vitamin D, can lead to toxicity. It is crucial to adhere to recommended dosages and consult with a veterinarian before adding supplements to a canine’s diet. A balanced approach ensures that the canine receives the appropriate nutrients without risking adverse effects.
Question 6: How does age affect a canine’s dietary needs in relation to shedding?
Age significantly affects a canine’s dietary needs. Senior canines may require diets with higher protein content to maintain muscle mass and support skin health. Additionally, age-related changes in metabolism and digestive function may necessitate adjustments to the dietary formulation. Consulting with a veterinarian is essential for tailoring the diet to the specific needs of the canine’s life stage.
In summary, managing canine shedding through diet involves a holistic approach that considers individual needs, breed predispositions, and overall health status. While dietary modifications can be effective, they are best implemented under the guidance of a qualified veterinary professional.
The subsequent section will explore specific dietary recommendations for various canine breeds known for excessive shedding.
Best Dog Food to Prevent Shedding
This exploration of optimal canine nutrition for minimizing hair loss has underscored several critical factors. The selection of what constitutes the “best dog food to prevent shedding” is not a singular solution, but rather a multifaceted approach. Key elements include adequate omega fatty acid intake, high-quality and digestible protein sources, antioxidant support, maintenance of hydration, strategic allergen avoidance, attention to breed-specific needs, and, fundamentally, prioritizing ingredient quality. The interplay of these factors significantly impacts the dermatological health of canines and directly influences the degree of shedding.
The information presented serves as a foundation for informed decision-making. Continued vigilance in monitoring canine coat condition, coupled with proactive consultation with veterinary professionals, will further refine nutritional strategies. As research advances and new dietary formulations emerge, a commitment to evidence-based practices will remain paramount in achieving sustained reductions in excessive canine hair loss and promoting overall well-being.


![Top-Rated: Best Golden Retriever Dog Food [2024 Guide] World’s Most Delicious Foods: Must-Try Dishes from Every Country Top-Rated: Best Golden Retriever Dog Food [2024 Guide] | World’s Most Delicious Foods: Must-Try Dishes from Every Country](https://lisasfoods.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-248-300x200.jpg)
![The BEST Dog Food for Pitbull Husky Mix [Guide] World’s Most Delicious Foods: Must-Try Dishes from Every Country The BEST Dog Food for Pitbull Husky Mix [Guide] | World’s Most Delicious Foods: Must-Try Dishes from Every Country](https://lisasfoods.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-246-300x200.jpg)