Selecting appropriate nourishment for a Belgian Malinois is a critical aspect of responsible ownership, directly impacting the canine’s overall health, performance, and longevity. The dietary needs of this breed are influenced by its high energy level, demanding exercise requirements, and predisposition to certain health conditions. Therefore, carefully considered food choices are essential to support optimal well-being.
Providing sustenance tailored to this breed offers numerous advantages. It helps maintain a healthy weight, supports robust muscle development and function, and contributes to a glossy coat. Historically, Malinois were bred as working dogs, requiring diets that could sustain their intense physical activity. Today, even as companion animals, their active nature necessitates a nutrient-rich diet capable of fueling their bodies and promoting vitality.
Consequently, the subsequent sections will explore key considerations when choosing canine nutrition, including optimal protein and fat content, appropriate carbohydrate sources, and the role of supplements. Special attention will be given to addressing common health concerns in the breed through dietary management, ultimately guiding owners toward making informed decisions regarding their Malinois’ dietary regimen.
Dietary Guidance for Belgian Malinois
The following recommendations aim to provide a framework for selecting a diet that supports the health and well-being of a Belgian Malinois. Considerations include nutritional content, specific breed needs, and common health concerns.
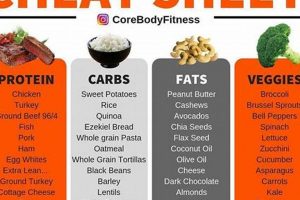
Tip 1: Prioritize High-Quality Protein Sources: A diet rich in animal-based protein is crucial for muscle development and maintenance. Look for foods where meat, poultry, or fish is listed as the first ingredient.
Tip 2: Assess Fat Content: Adequate fat intake supports energy levels and coat health. Opt for foods with a moderate fat content, derived from sources like fish oil or poultry fat.
Tip 3: Scrutinize Carbohydrate Sources: Select easily digestible carbohydrates like sweet potatoes or brown rice. Avoid foods with excessive amounts of corn, wheat, or soy, as these can be potential allergens or difficult to process.
Tip 4: Consider Activity Level: Adjust the food quantity according to the canine’s activity level. More active Malinois require higher caloric intake to maintain a healthy weight.
Tip 5: Monitor for Allergies and Sensitivities: Observe for signs of food allergies, such as skin irritation or digestive upset. If suspected, consider a limited-ingredient diet or consult with a veterinarian.
Tip 6: Supplement Strategically: Depending on individual needs, supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can support joint health, particularly important for this active breed.
Tip 7: Consult with a Veterinarian or Veterinary Nutritionist: A professional assessment can provide tailored dietary recommendations based on the dog’s specific health history and needs.
Adhering to these guidelines contributes to optimal health, performance, and longevity. It fosters strong muscles, a healthy weight, and a vibrant coat, all essential for this breed.
The following sections will discuss specific dietary considerations for Belgian Malinois with sensitivities or health conditions, furthering the discussion of optimal nutrition.
1. High protein content
The robust muscular structure and high activity levels inherent in the Belgian Malinois breed necessitate a diet characterized by substantial protein content. This macronutrient plays a pivotal role in muscle tissue repair and development, crucial for maintaining the physical prowess expected of this working dog. Inadequate protein intake can lead to muscle wasting, reduced stamina, and impaired overall performance. Consequently, the selection of canine nutrition must prioritize animal-based protein sources, such as meat, poultry, or fish, to meet the metabolic demands unique to the breed.
For instance, a Malinois engaged in Schutzhund training or law enforcement work requires significantly higher protein levels compared to a less active companion animal. A real-life example would be a working Malinois consuming a diet with at least 30% protein, demonstrating superior muscle mass and endurance compared to a similar dog fed a lower protein diet. Furthermore, sufficient protein intake supports the synthesis of enzymes and hormones essential for various physiological processes, further highlighting its importance in maintaining overall health.
In summation, high protein content is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for optimal health and performance in Belgian Malinois. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to make informed dietary choices, ensuring the canine’s nutritional needs are adequately met. This knowledge empowers owners to proactively support their dog’s physical well-being, fostering a longer, healthier, and more productive life. Diets deficient in protein can ultimately undermine the breed’s inherent capabilities and predispose it to various health problems.
2. Appropriate fat levels
Dietary fat plays a critical role in the health and performance of a Belgian Malinois, contributing significantly to its energy supply, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being. As a highly active breed with substantial energy demands, the Malinois relies on fat as a concentrated source of calories. Insufficient fat intake can lead to weight loss, reduced stamina, and a dull coat. Conversely, excessive fat can contribute to obesity and associated health problems. Therefore, finding the correct balance is essential when selecting canine nutrition.
The “appropriate fat levels” in canine sustenance directly impact the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), vital for immune function, bone health, and vision. A diet formulated with quality fat sources, such as fish oil or poultry fat, supports optimal nutrient uptake. An example illustrating this connection is the observation that Malinois fed diets with insufficient fat exhibit dry skin and a lackluster coat, signs of inadequate vitamin absorption. Conversely, controlled fat intake, combined with regular exercise, aids in maintaining a lean body mass, crucial for agility and performance in working dogs.
In summary, appropriate fat levels are an indispensable component of canine nutrition for the Belgian Malinois. Understanding the relationship between fat intake, energy requirements, and nutrient absorption enables informed decisions regarding dietary choices. Maintaining this balance presents a challenge, requiring careful assessment of the individual dog’s activity level, metabolism, and overall health status. By prioritizing quality fat sources and monitoring the canine’s physical condition, owners can effectively support their Malinois’ energy demands and promote optimal health.
3. Digestible carbohydrates
The inclusion of digestible carbohydrates in canine nutrition is a critical factor when determining the suitability of a diet for a Belgian Malinois. Carbohydrates serve as a significant energy source, providing the necessary fuel for this breed’s characteristic high activity levels. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal; digestibility is paramount. Indigestible carbohydrates can lead to gastrointestinal distress, nutrient malabsorption, and reduced overall performance. Therefore, selecting canine nutrition with a focus on readily digestible carbohydrate sources becomes imperative for this breed.
Digestible carbohydrates, such as sweet potatoes, brown rice, and oats, are efficiently broken down and absorbed by the canine digestive system. This contrasts with less digestible options like corn, wheat, or soy, which may cause digestive upset in sensitive dogs. For example, a Malinois participating in agility training requires sustained energy; a diet featuring digestible carbohydrates ensures a steady release of glucose, preventing energy crashes and supporting optimal performance. In practice, observing the canine’s stool quality can indicate carbohydrate digestibility; well-formed stools suggest efficient digestion and absorption, while loose stools may indicate the opposite. The absence of excessive flatulence is also a positive indicator.
In conclusion, the selection of canine nutrition for a Belgian Malinois should prioritize digestibility of carbohydrates. This approach not only supports the canine’s energy demands but also minimizes the risk of gastrointestinal issues and promotes efficient nutrient utilization. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to proactively manage the canine’s health and performance through informed dietary choices. The challenge resides in identifying and sourcing sustenance with a favorable carbohydrate profile, demanding diligent label reading and potentially consultation with a veterinary professional.
4. Joint health support
Maintaining optimal joint health is a paramount consideration when selecting sustenance for a Belgian Malinois. This breed, known for its athleticism and high activity levels, places considerable stress on its joints, predisposing it to conditions like hip and elbow dysplasia, as well as osteoarthritis. Therefore, canine nutrition should incorporate components that proactively support joint integrity and function.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin Supplementation
Glucosamine and chondroitin are naturally occurring compounds that contribute to the structural integrity of cartilage. Supplementation with these substances supports cartilage regeneration and reduces inflammation within the joints. For instance, a canine nutrition formulation including these additives may slow the progression of osteoarthritis in a Malinois with a predisposition to joint issues. Their incorporation into the diet serves as a preventative measure, mitigating potential long-term joint damage resulting from intense physical activity.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), possess anti-inflammatory properties that benefit joint health. These fatty acids can modulate the inflammatory response within joints, reducing pain and improving mobility. Incorporating fish oil, a rich source of omega-3s, into the diet of a Malinois can alleviate symptoms associated with arthritis and enhance joint flexibility. This aspect of canine nutrition represents a non-pharmaceutical approach to managing joint inflammation and promoting long-term joint health.
- Weight Management
Maintaining an optimal body weight is crucial for minimizing stress on the joints. Excess weight places undue strain on cartilage and supporting structures, accelerating the degenerative process. Canine nutrition should promote a lean body mass, preventing obesity and reducing the risk of joint-related complications. Portion control and a balanced macronutrient profile contribute to effective weight management, safeguarding joint health and preserving mobility throughout the Malinois’ life.
- Antioxidant Inclusion
Oxidative stress plays a role in the development and progression of joint disease. Incorporating antioxidants, such as Vitamin E and Vitamin C, into canine nutrition can help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage within the joints. These antioxidants protect cartilage cells from degradation, contributing to long-term joint health and delaying the onset of age-related joint problems. The synergistic effect of multiple antioxidants provides a comprehensive defense against oxidative stress, supporting joint integrity and function.
These facets highlight the interconnectedness between canine nutrition and joint health support in the Belgian Malinois. By incorporating glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, alongside careful weight management, sustenance can proactively address joint health concerns. This holistic approach to canine nutrition not only supports the breed’s inherent athleticism but also mitigates the risk of debilitating joint conditions, ensuring a higher quality of life for the Malinois.
5. Limited ingredient options
The selection of canine nutrition for a Belgian Malinois frequently necessitates consideration of limited ingredient options. This dietary approach addresses sensitivities and allergies prevalent in the breed, enabling effective management of adverse reactions and promotion of overall health. The relationship between limited ingredient options and optimal nutrition in this breed is thus a critical aspect of responsible ownership.
- Identification of Allergens
Limited ingredient diets simplify the identification of allergens by reducing the number of potential causative agents. Common allergens such as corn, wheat, soy, and certain animal proteins are excluded. The absence of these ingredients allows owners to isolate the specific triggers of adverse reactions. For example, a Malinois exhibiting skin irritation may find relief through a diet eliminating common poultry sources, pinpointing an allergy to chicken. This targeted approach streamlines the diagnostic process, facilitating effective dietary management.
- Reduction of Gastrointestinal Distress
Belgian Malinois can experience gastrointestinal sensitivity to certain ingredients, leading to diarrhea, vomiting, or flatulence. Limited ingredient diets mitigate these issues by minimizing the inclusion of potential irritants. This reduces the digestive burden and promotes efficient nutrient absorption. An illustrative case is a Malinois with a history of frequent digestive upset experiencing improved stool consistency and reduced discomfort on a limited ingredient diet. This demonstrates the positive impact of simplifying the dietary composition on gastrointestinal health.
- Minimization of Additives and Fillers
Many conventional canine nutrition options contain artificial additives, preservatives, and fillers that can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive dogs. Limited ingredient diets typically exclude these non-essential components, focusing on whole, natural ingredients. This reduces the risk of exposure to potentially harmful substances and promotes a more wholesome dietary approach. A Malinois with a history of skin allergies may demonstrate a significant improvement in skin condition when switched to a diet free of artificial colors and preservatives.
- Support for Elimination Diets
Veterinarians often recommend elimination diets to diagnose food allergies or intolerances in dogs. These diets involve feeding a limited number of novel protein and carbohydrate sources to identify specific triggers. Limited ingredient formulations are ideally suited for this purpose, providing a controlled dietary environment for accurate diagnosis. A Malinois undergoing an elimination trial might be fed a diet consisting solely of venison and sweet potato, allowing for the identification of potential allergies to more common ingredients.
In conclusion, limited ingredient options represent a valuable tool in managing canine nutrition for the Belgian Malinois, particularly in cases of allergies, sensitivities, or gastrointestinal issues. By simplifying the ingredient list and eliminating potential irritants, these diets promote improved health and well-being. Careful consideration of ingredient sourcing and formulation remains essential to ensure adequate nutrient provision, highlighting the need for informed dietary choices.
6. Breed-specific formulas
The concept of breed-specific formulas in canine nutrition aims to address the unique physiological and metabolic requirements inherent in different breeds. For a Belgian Malinois, such formulas should ideally consider the breed’s high energy expenditure, propensity for certain musculoskeletal conditions, and digestive sensitivities. Therefore, the effectiveness of breed-specific formulas as the “best dog food for a belgian malinois” depends on the degree to which the formulation precisely targets these particular needs. In essence, breed specificity becomes a valuable attribute only when it translates to tangible health benefits for the canine.
The rationale behind breed-specific formulas lies in the observed variations in nutrient utilization and metabolic processes across breeds. For example, larger breeds often benefit from controlled calcium and phosphorus levels to support healthy bone development and minimize the risk of skeletal disorders. In the case of a Malinois, a breed-specific formula might incorporate higher protein levels for muscle maintenance, along with joint support supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin. However, it is essential to evaluate the scientific evidence supporting the claims of breed-specific superiority, ensuring the benefits are demonstrable and not merely marketing assertions. A real-life example might be a Malinois fed a breed-specific formula exhibiting improved muscle mass and endurance during agility training compared to a dog fed a generic adult dog food. If the breed-specific feed is found to have caused bloating or allergies on a wide scale then it is not suitable.
While breed-specific formulas offer a potentially advantageous approach to canine nutrition, critical evaluation of their composition and purported benefits remains paramount. The effectiveness hinges on the precise alignment of the formulation with the specific physiological demands of the Belgian Malinois. Challenges include the variability in individual canine needs and the potential for overgeneralization within the breed. Ultimately, the selection of the most appropriate food for a Malinois involves a combination of factors, including individual health status, activity level, and veterinary guidance, ensuring the breed-specific formula truly contributes to optimal health and performance.
7. Calorie density
Calorie density represents a critical characteristic of sustenance selection for a Belgian Malinois, profoundly impacting the canine’s energy levels, weight management, and overall physical condition. Given this breed’s high activity level and demanding energy expenditure, the caloric concentration within a food source directly influences the quantity required to meet daily metabolic needs. Optimizing calorie density is thus essential for maintaining a healthy weight, supporting performance, and preventing both undernourishment and obesity.
- Energy Expenditure Matching
The calorie density must align with the canine’s daily energy expenditure. A working Malinois involved in police work or herding requires a higher calorie density to fuel its intense physical activity. Conversely, a less active Malinois needs a lower calorie density to prevent weight gain. For example, a highly active Malinois may need a food with 450 kcal per cup, while a less active one may thrive on a food with 350 kcal per cup. Failure to match caloric intake with expenditure results in either insufficient energy for optimal performance or excessive calorie storage as fat.
- Portion Control and Satiety
Calorie density affects the portion size needed to satisfy the canine’s appetite. High-calorie density foods require smaller portions, which may not provide sufficient satiety, potentially leading to begging or food-seeking behavior. Lower-calorie density foods allow for larger portions, promoting a feeling of fullness. A Malinois fed a low-calorie density food may feel more satiated than one fed a high-calorie density food, even if the total caloric intake is the same. This facet is significant for managing hunger and preventing overeating.
- Impact on Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
The concentration of calories can influence digestive efficiency and nutrient absorption. Highly processed, calorie-dense foods may be less digestible than whole-food, lower-calorie density options. A diet with a high concentration of readily digestible ingredients ensures optimal nutrient uptake, crucial for a Malinois’ health and performance. A real-world example involves observing stool quality: a Malinois thriving on a digestible, calorie-appropriate food will exhibit firm, well-formed stools, indicative of efficient nutrient absorption.
- Ingredient Quality and Calorie Source
The source of calories matters. Calorie density derived from high-quality protein and healthy fats is preferable to that from simple carbohydrates or fillers. A Malinois’ diet should prioritize animal-based protein and healthy fats for sustained energy and muscle maintenance. A diet reliant on low-quality fillers contributes to empty calories and may lead to nutrient deficiencies. Therefore, scrutinizing the ingredient list alongside the calorie density is essential for selecting a nutritionally balanced food.
Calorie density is thus not merely a numerical value but a comprehensive indicator of sustenance suitability for a Belgian Malinois. Effective utilization of this information, combined with an understanding of individual canine needs, facilitates informed dietary choices that optimize health, performance, and longevity. Balancing calorie density with ingredient quality and portion control represents a fundamental aspect of responsible canine nutrition.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the dietary needs and nutritional management of Belgian Malinois. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance on selecting appropriate sustenance for this breed.
Question 1: What constitutes an optimal protein percentage in the diet of a Belgian Malinois?
An optimal protein percentage typically falls within the range of 25-30% on a dry matter basis. The specific percentage may vary depending on the individual canine’s activity level and life stage, necessitating careful consideration of individual needs.
Question 2: Are grain-free diets inherently superior for Belgian Malinois?
Grain-free diets are not inherently superior. While some Malinois may exhibit sensitivities to certain grains, many tolerate them well. The focus should be on ingredient quality and digestibility rather than simply eliminating grains altogether.
Question 3: How frequently should a Belgian Malinois be fed per day?
Most adult Belgian Malinois benefit from being fed twice daily. This feeding schedule helps maintain consistent energy levels and reduces the risk of bloat, a concern in some deep-chested breeds.
Question 4: Is supplementation with glucosamine and chondroitin necessary for all Belgian Malinois?
Supplementation with glucosamine and chondroitin is not necessary for all Malinois, but it may be beneficial, particularly for active dogs or those with a predisposition to joint problems. Veterinary consultation is recommended before initiating supplementation.
Question 5: How can food allergies be effectively identified in a Belgian Malinois?
Food allergies are best identified through a veterinarian-supervised elimination diet. This involves feeding a novel protein and carbohydrate source for a specified period, followed by the gradual reintroduction of individual ingredients to pinpoint potential allergens.
Question 6: What role do omega-3 fatty acids play in canine nutrition for this breed?
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to coat health, reduce inflammation, and support cognitive function. Supplementation with fish oil, a rich source of omega-3s, can be beneficial for many Belgian Malinois.
The information presented underscores the importance of individualized dietary management, emphasizing that no single approach is universally suitable. Veterinary consultation is always recommended to tailor sustenance to the specific needs of each canine.
The ensuing sections will delve into specific feeding strategies for different life stages of a Belgian Malinois, providing further insights into optimal nutrition.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has illuminated the multifaceted considerations involved in selecting the most appropriate sustenance for a Belgian Malinois. Key determinants, encompassing protein content, fat levels, carbohydrate digestibility, joint health support, and the potential benefits of limited ingredient or breed-specific formulations, have been scrutinized. Effective dietary management necessitates a thorough understanding of these factors, coupled with careful assessment of individual canine needs. Calorie density, portion control, and the identification of potential allergies represent further crucial aspects of responsible feeding practices.
The optimal approach involves a proactive and informed methodology, prioritizing veterinary guidance and ongoing monitoring of the canine’s health and well-being. Sustained diligence in dietary management contributes significantly to the Belgian Malinois’ overall quality of life, fostering optimal performance, longevity, and the mitigation of breed-specific health concerns. Therefore, continued dedication to informed feeding practices remains paramount for responsible ownership and the enduring vitality of this exceptional breed.